Oz Andrews
Director
Tyba Home
We use the Geomiq platform as it is the easiest and fastest way to get any of our parts made. They are the obvious choice, highly recommended!
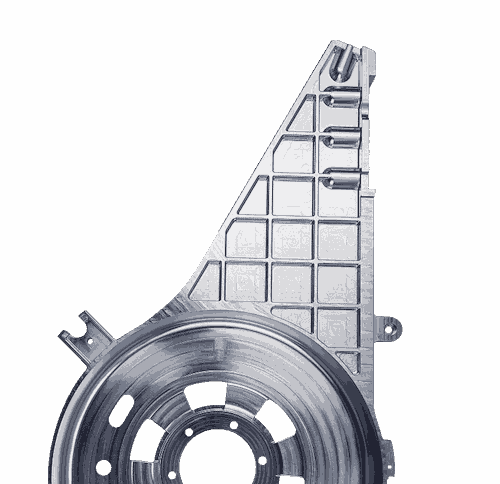
CNC prototyping or production, we offer world-class CNC machined parts delivered to your door as little as 5 days. With a huge variety of CNC machining materials and secondary finishes available you can be sure to get what you need.
All uploads are secure and confidential.
Trusted by






At Geomiq, we're experts in CNC machining production and prototyping, ready to meet your specific needs. Whether you're after precision for smaller quantities or large-scale production, our services are tailored just for you.
Multi-axis 3 & 5 axis CNC machining from our global supply chain provides one-off prototypes to large-scale production, ensuring consistent quality and lead times.
CNC Turning from our global supply chain offers one-off CNC prototypes to large-scale production.
EDM spark and Wire erosion available for high-precision cutting and shapes that are unable to be cut by a rotating mill. With tolerances down to as little as +/- 0.001mm we can produce parts that have both milled, turned and EDM machined features. Lead times from 7 days allows rapid turnaround for your projects.
Geomiq provides premier CNC machining services in the UK, proudly partnering with 1100+ highly vetted CNC specialists. With their proven track record in crafting high-quality mechanical parts globally, coupled with our team's expertise and commitment to rigorous quality assurance, you can trust Geomiq to deliver flawless CNC machined parts every time.
Order now for CNC machined parts arriving in as little as 5 days!
Achieve precision with our standard CNC tolerance of +/- 0.127mm, configurable for machining down to +/- 0.005mm.
Geomiq's top-notch supply chain ensures competitive prices, whether you need a one-off CNC machining prototype or 10,000 units.
Elevate your CNC Machined parts with high-quality finishing processes, including anodising, polishing, plating, powder coating, and more.
Choose from over 100 plastic and metal CNC machining materials, carefully selected for each part. Contact us if the material you need is not listed.
Rely on our world-class supply chain to meet diverse CNC machining requirements.
Upload your CAD to our platform, select your lead time and get an instant or 24hr CNC quote.
We select the most suited manufacturer for your order, with production starting immediately.
We guarantee your order arrives to specification, with our industry leading virtual and physical quality standards.
We ship your parts on express services where possible, including physical delivery notes and inspection reports.
Upload your CAD to our platform, select your lead time and get an instant or 24hr CNC quote.
We select the most suited manufacturer for your order, with production starting immediately.
We guarantee your order arrives to specification, with our industry leading virtual and physical quality standards.
We ship your parts on express services where possible, including physical delivery notes and inspection reports.
We are committed to offering the best quality assurance in the business. Our highly skilled engineers triple-check all your files and parts, from the initial quote to the final inspection, ensuring your satisfaction the first time, every time.
At Geomiq, we understand the value of your time, and we are dedicated to helping you save more of it. Upon uploading your files, we provide a quote within one business day, and our network of highly experienced partners ensures the finished CNC products are of the highest quality with short lead times.
We collaborate with 180+ highly vetted and experienced CNC manufacturers from various countries. This allows you to access a world-class supply chain, offering greater capabilities and the highest standards globally, all from a single access point.
See all finishes
Filter By:
As machined finish is a raw finish that displays machining marks from the machining process. As standard we machine to 3.2Ra, however you can specify the surface roughness down to 0.2Ra.
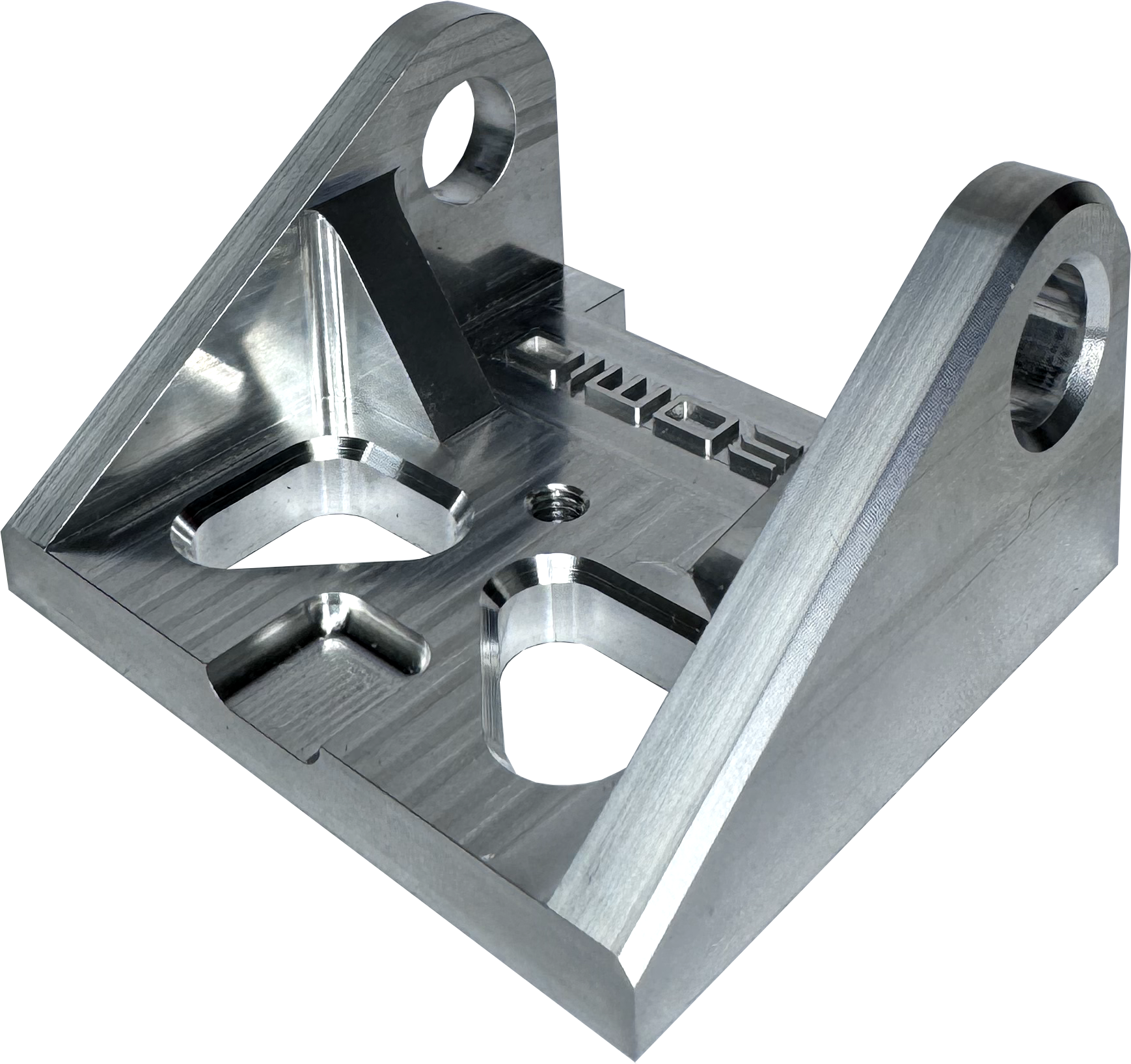

Visible tooling marks and light surface scratches.
The examples below have been bead blasted, acid cleaned for pre-treatment and hot water sealed. They offer a consistent cosmetic finish and is the most popular finishing method for most aluminium parts. We offer 30 - 220 grit bead blasting, aqua blasting and all colours of anodising including colour matching.
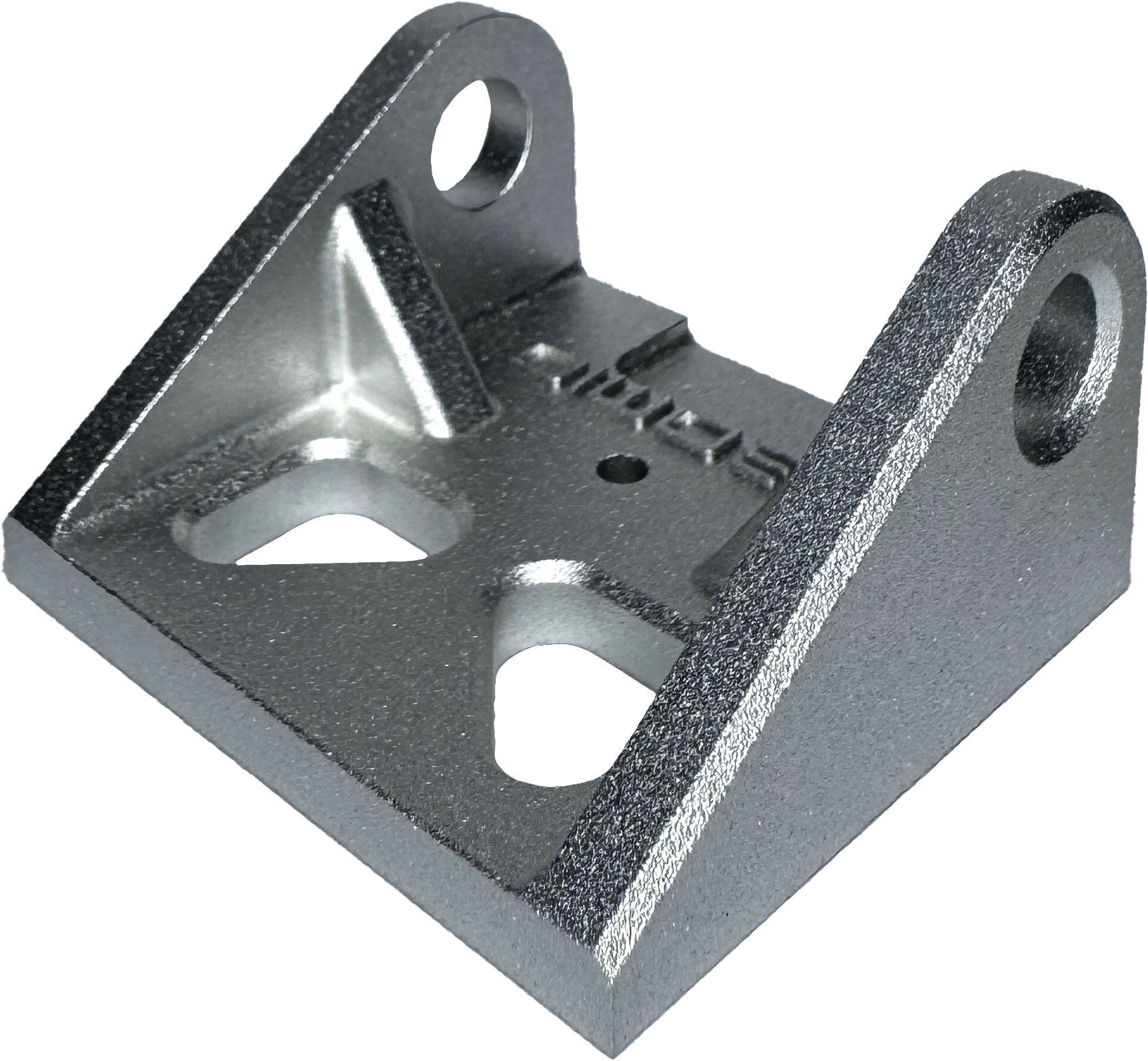

Removes all machining marks and leaves heavy texture
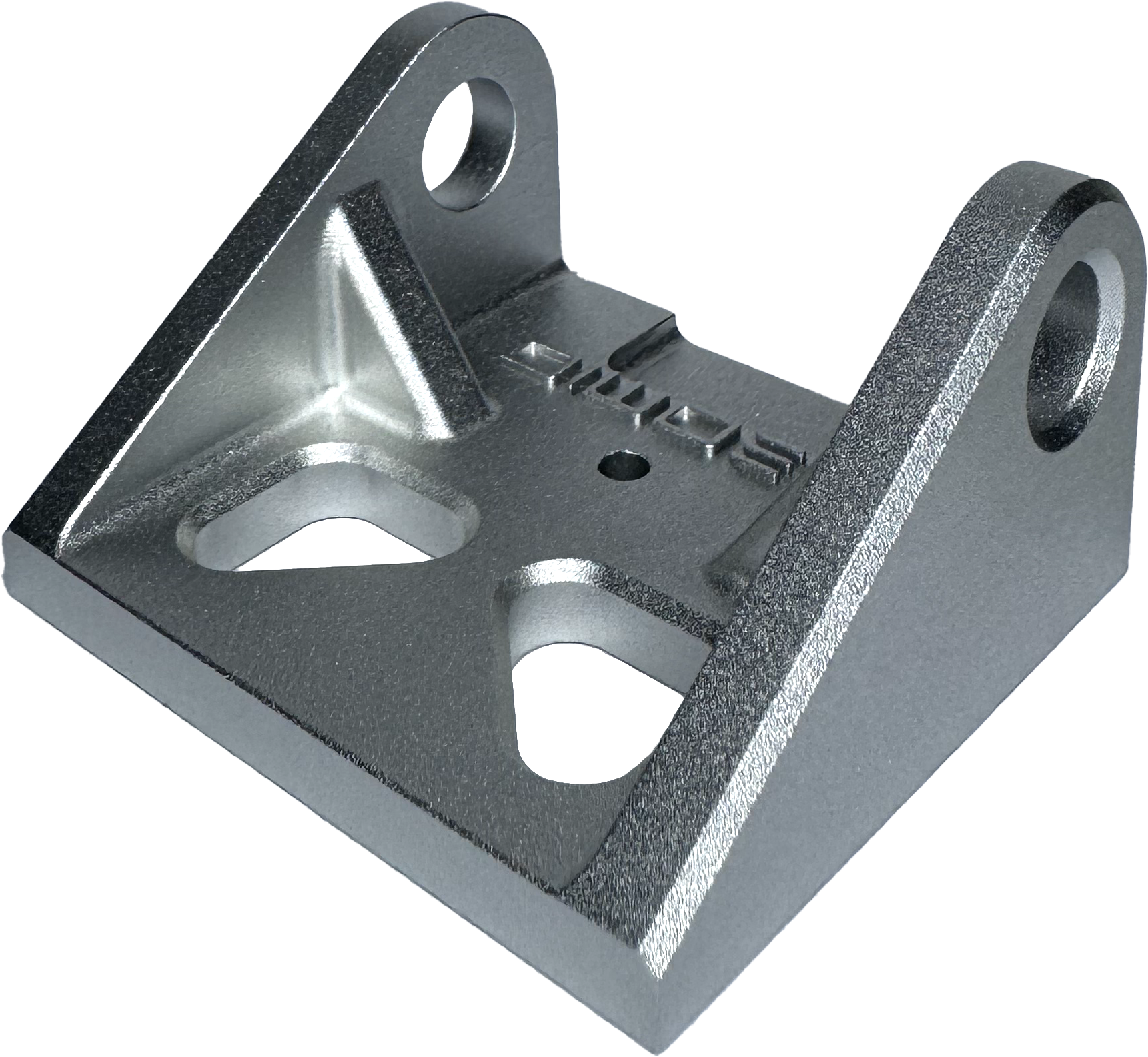

Removes all machining marks and leaves heavy texture
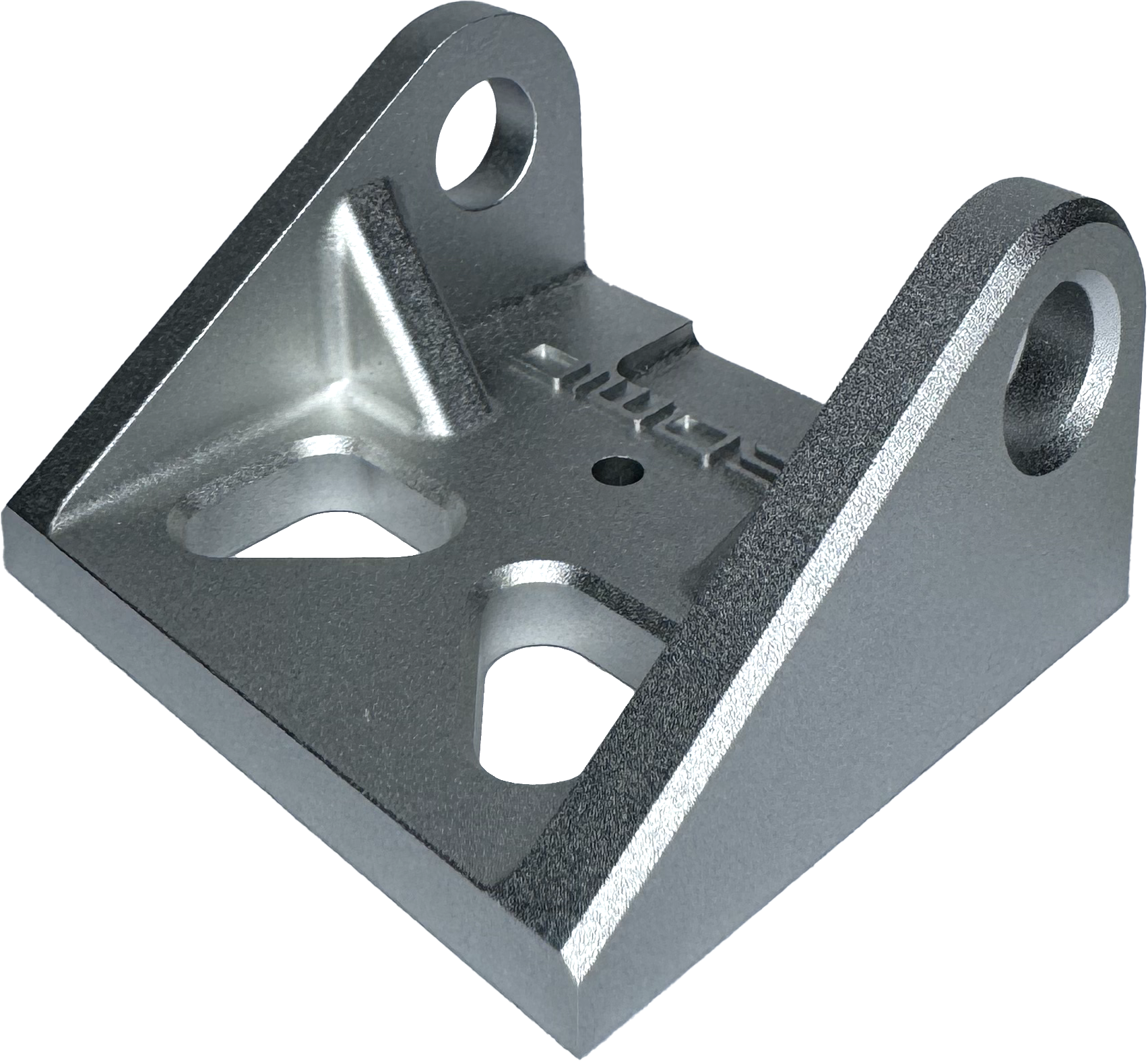

Removes all machining marks and leaves medium texture
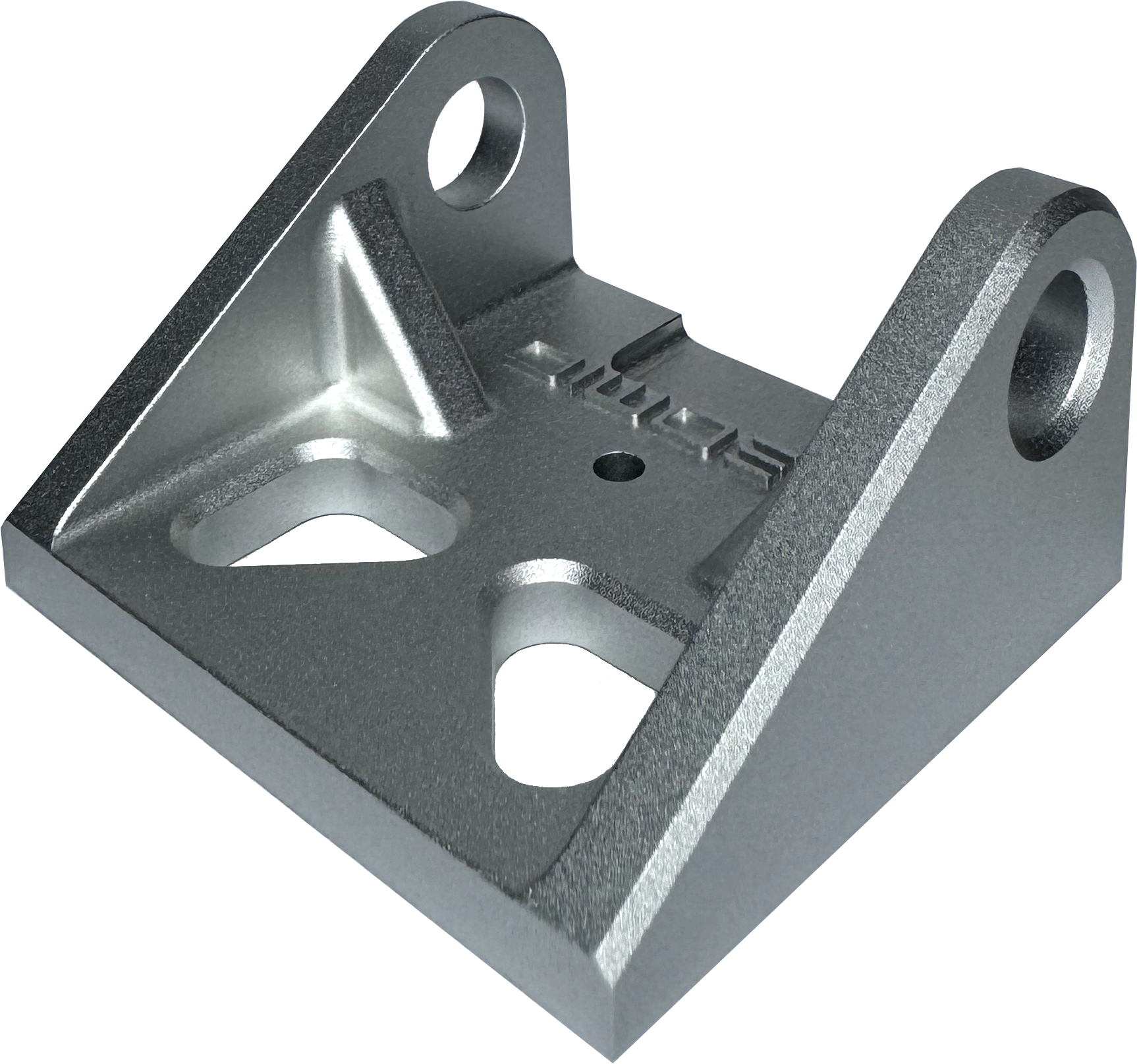
(Most common) Removes all machining marks & medium texture
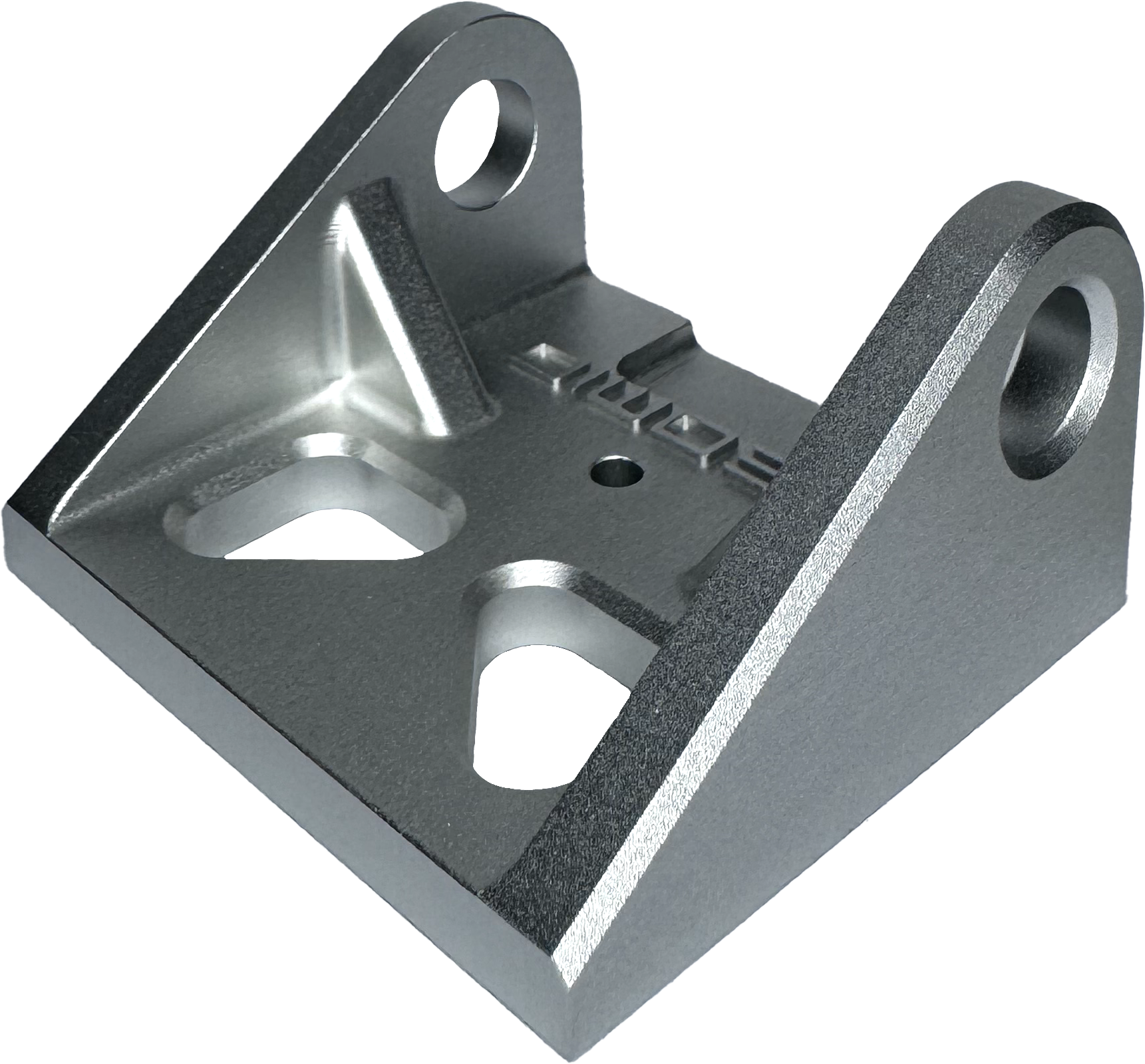

Removes most machining marks and leaves medium texture
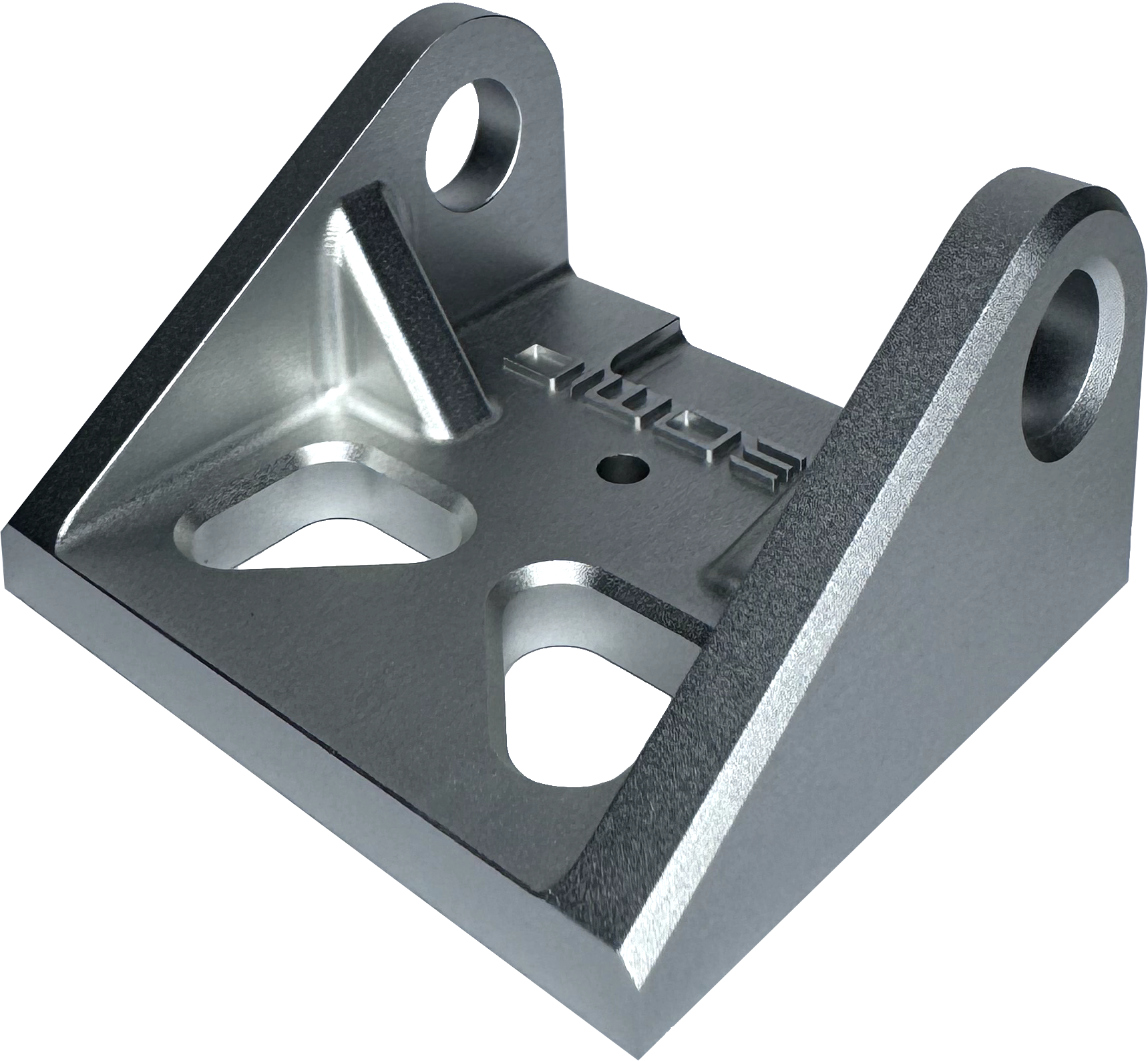

Removes medium machining marks and leaves medium-soft texture
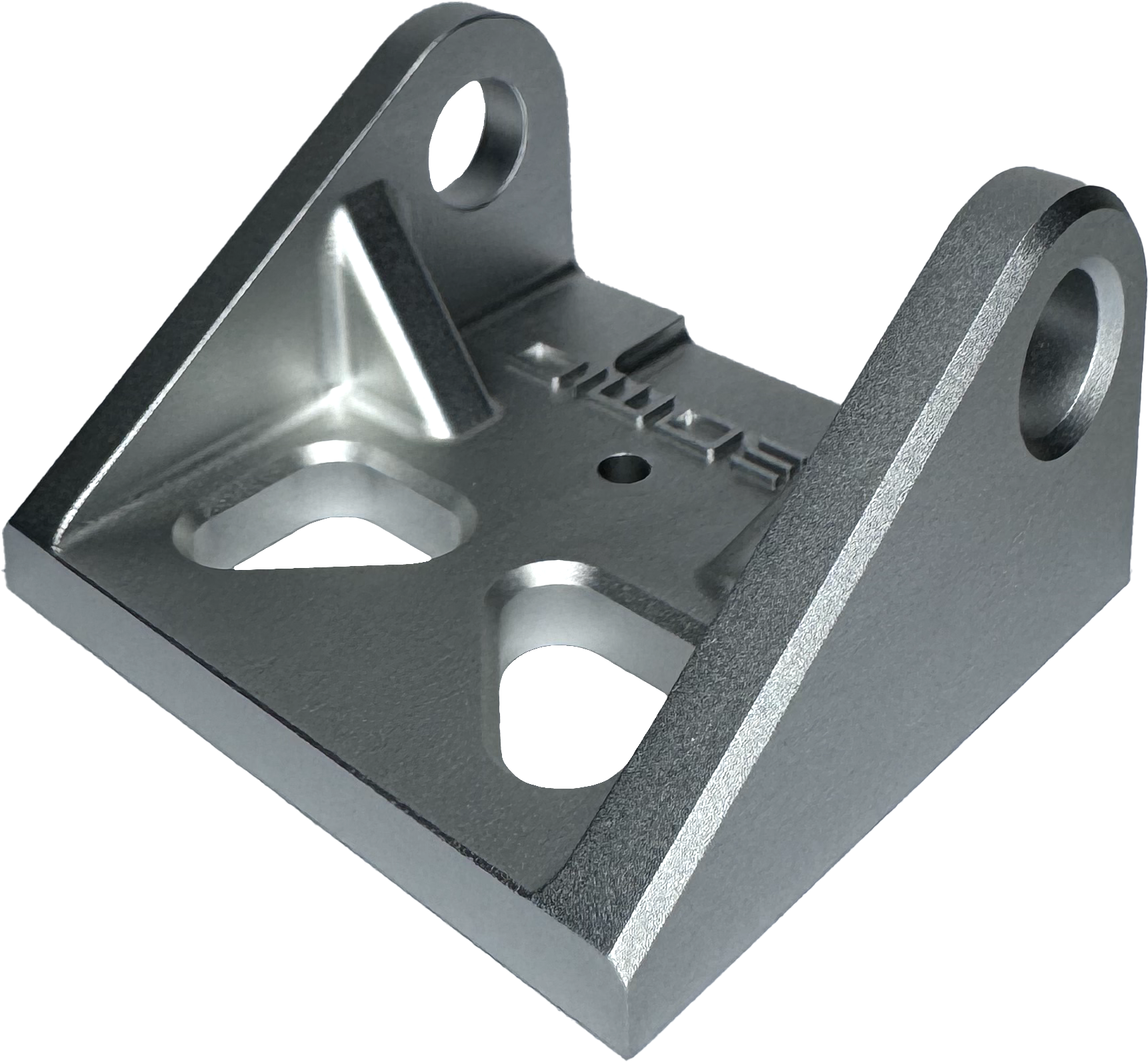

Removes light machining marks and leaves medium-soft texture
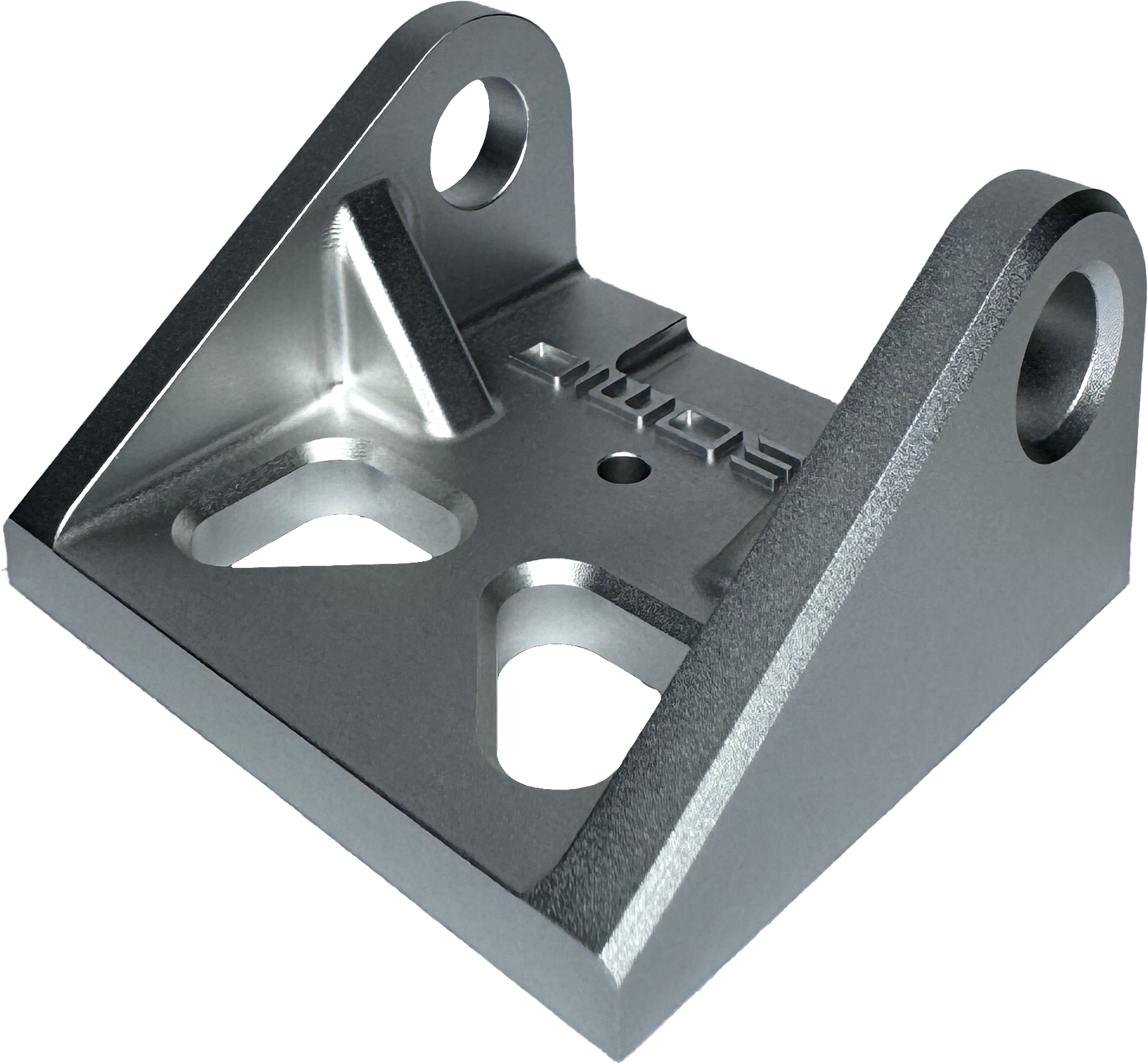

Removes light machining marks and leaves soft texture
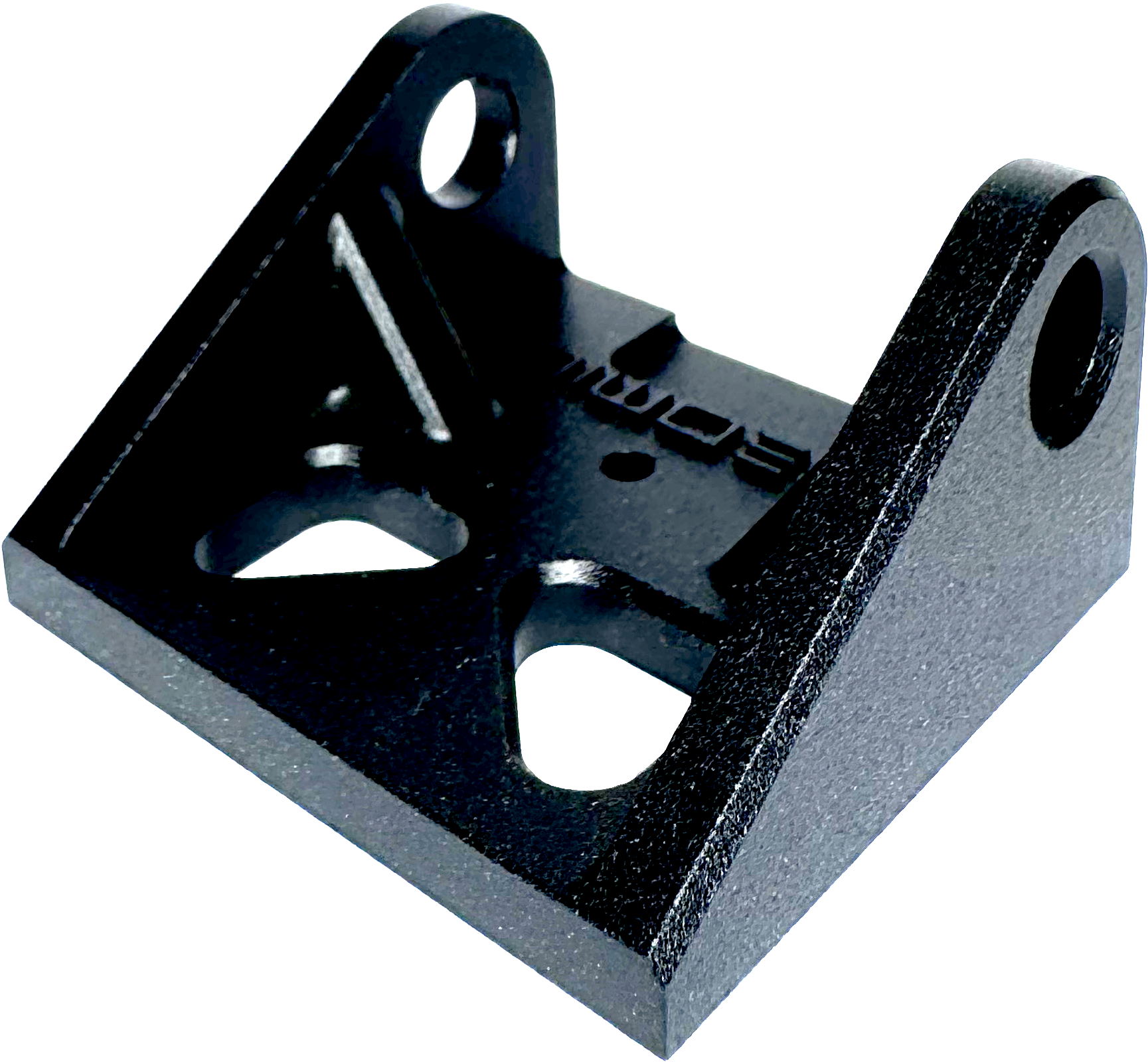

Removes all machining marks and leaves heavy texture
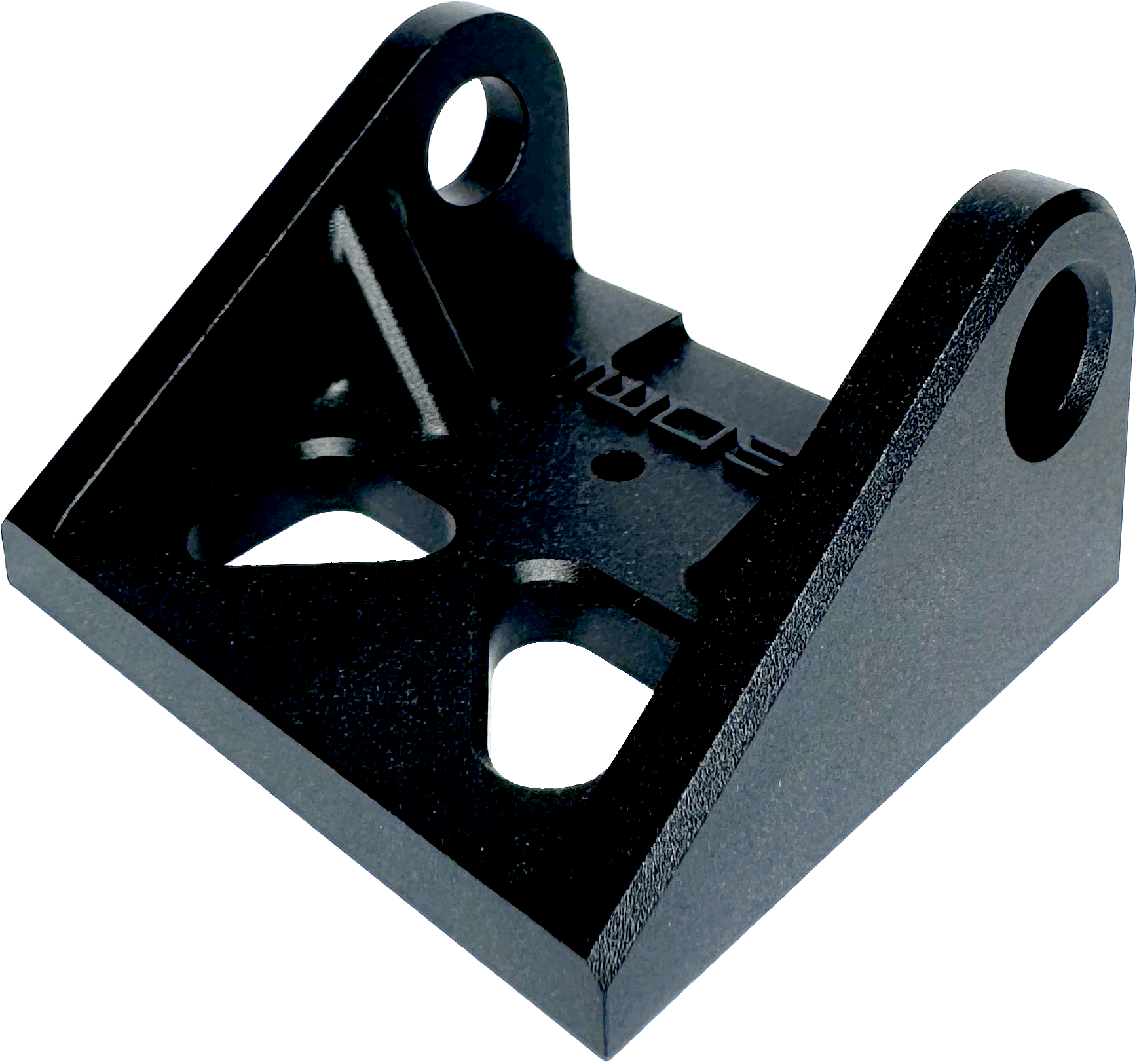

Removes all machining marks and leaves heavy texture
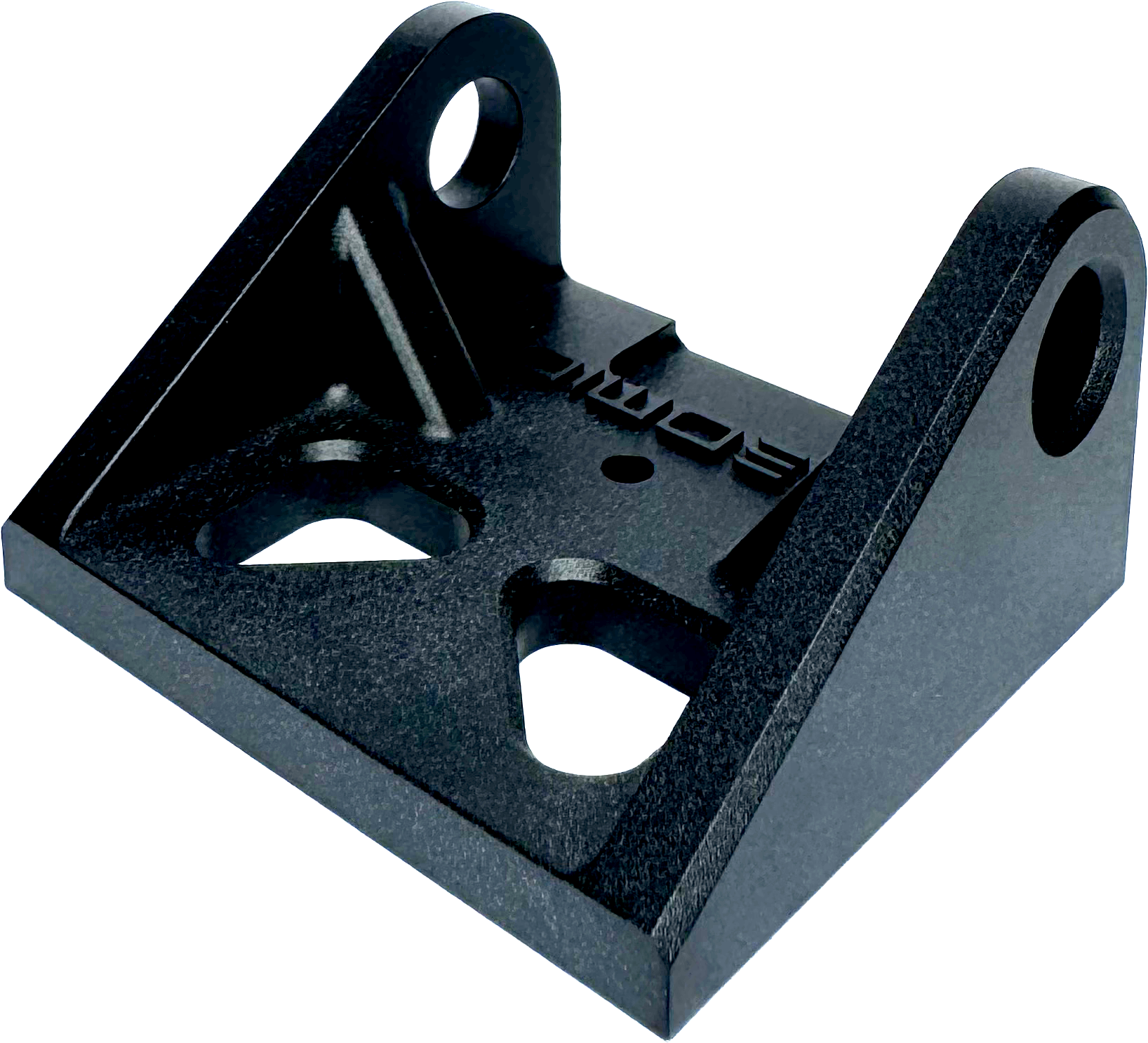
Removes all machining marks and leaves medium texture
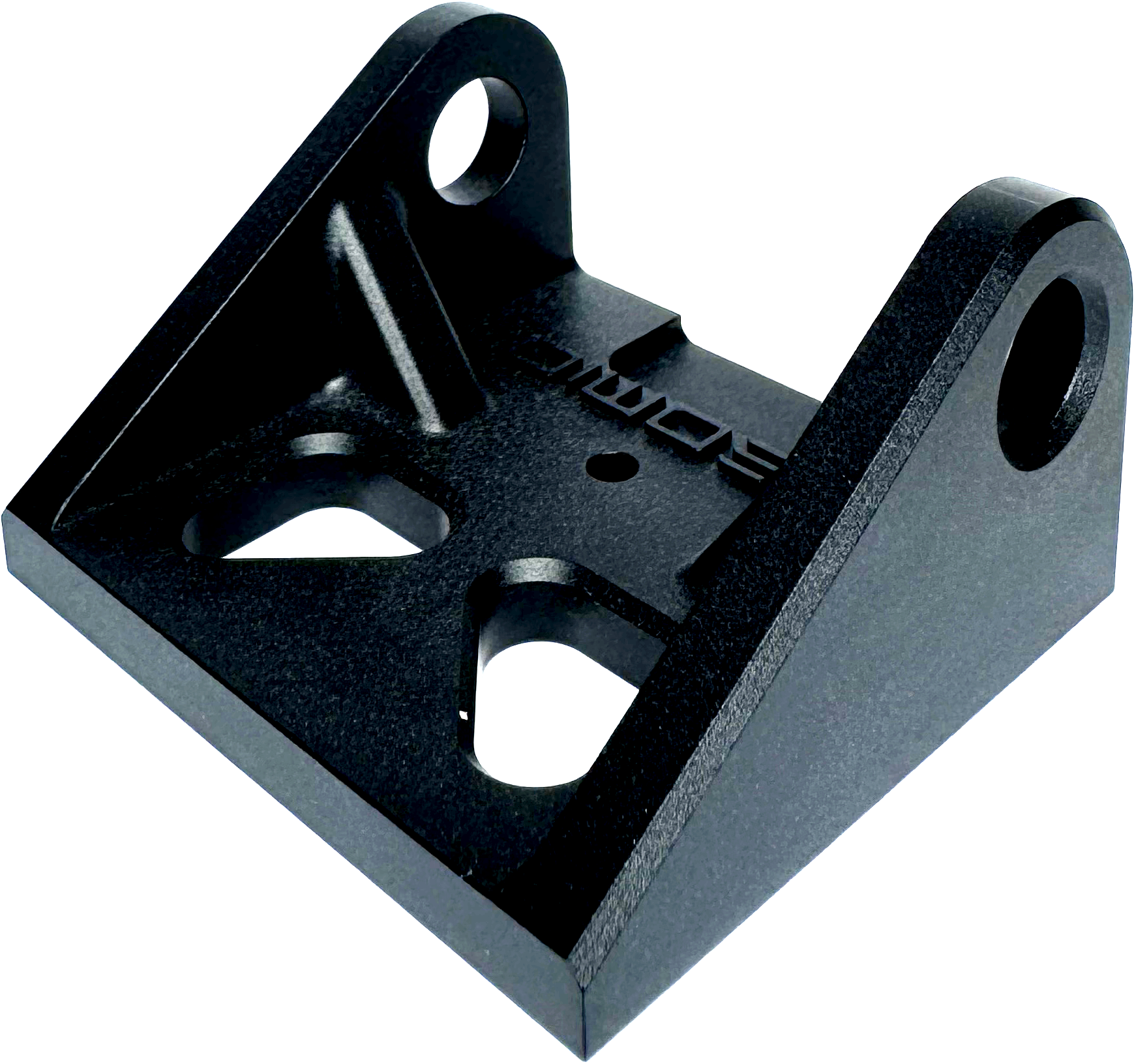
(Most common) Removes all machining marks & medium texture

Removes most machining marks and leaves medium texture

Removes medium machining marks and leaves medium-soft texture

Removes light machining marks and leaves medium-soft texture
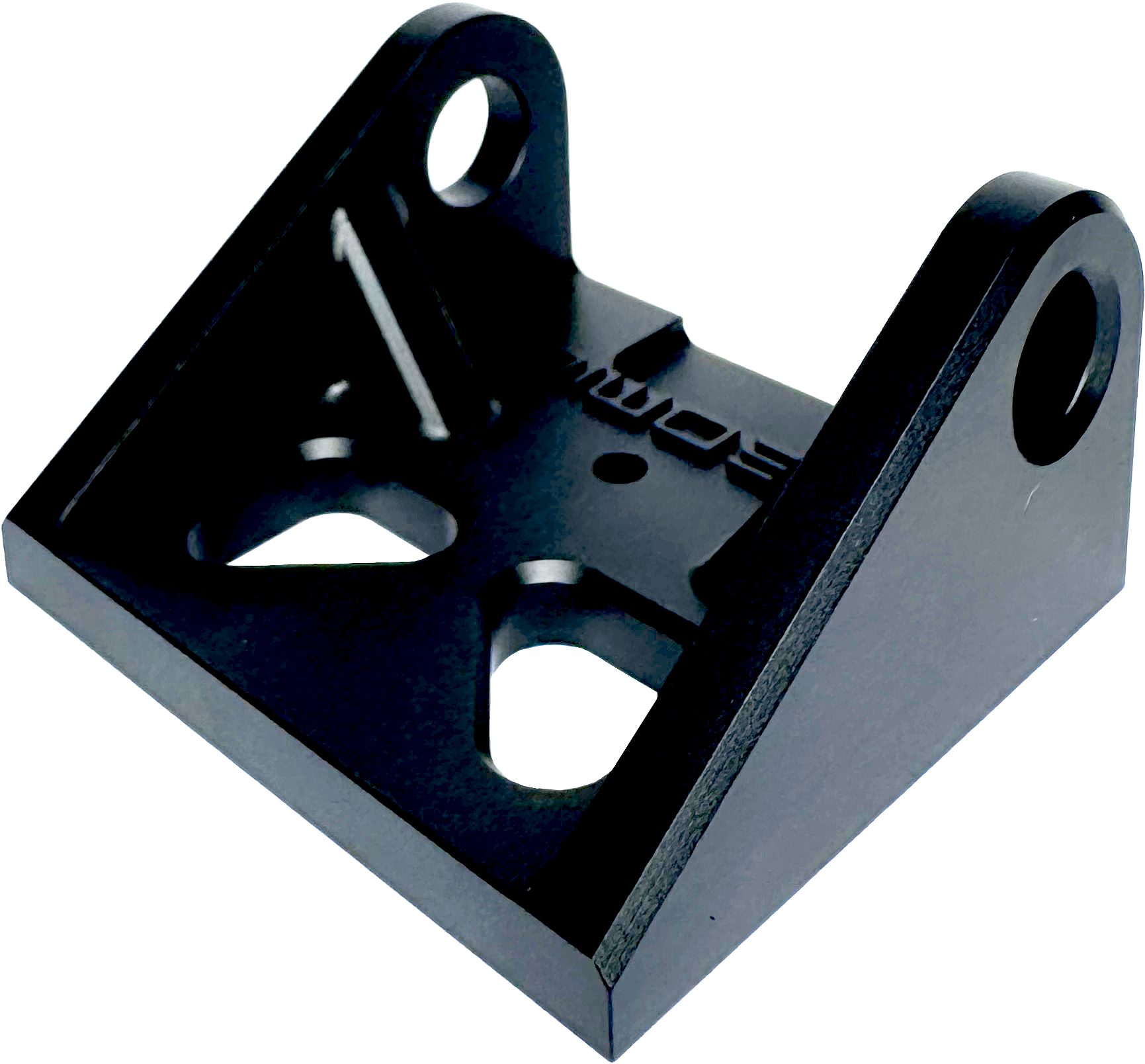

Removes light machining marks and leaves soft texture
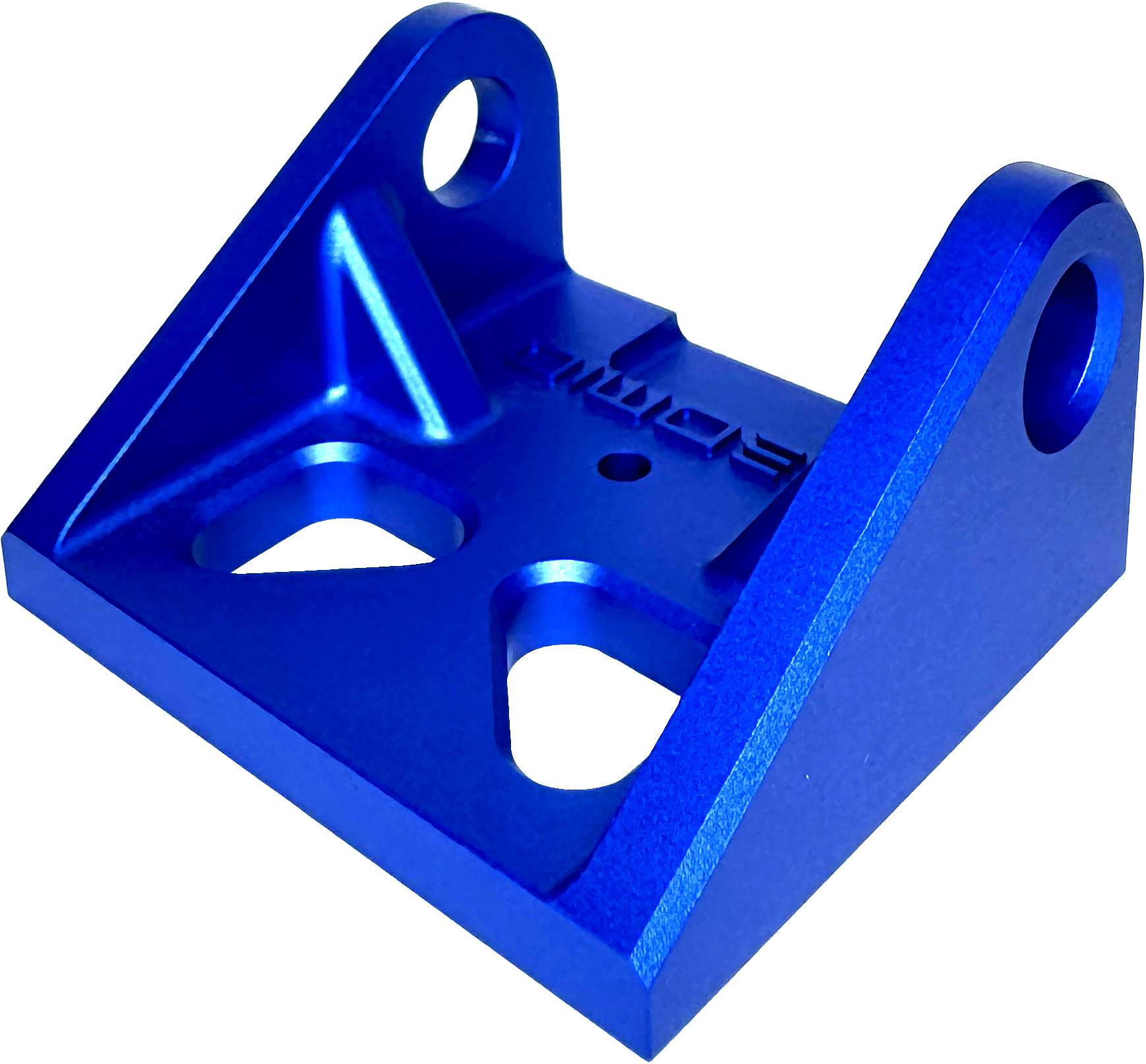

Removes all machining marks & medium texture with added blue dye
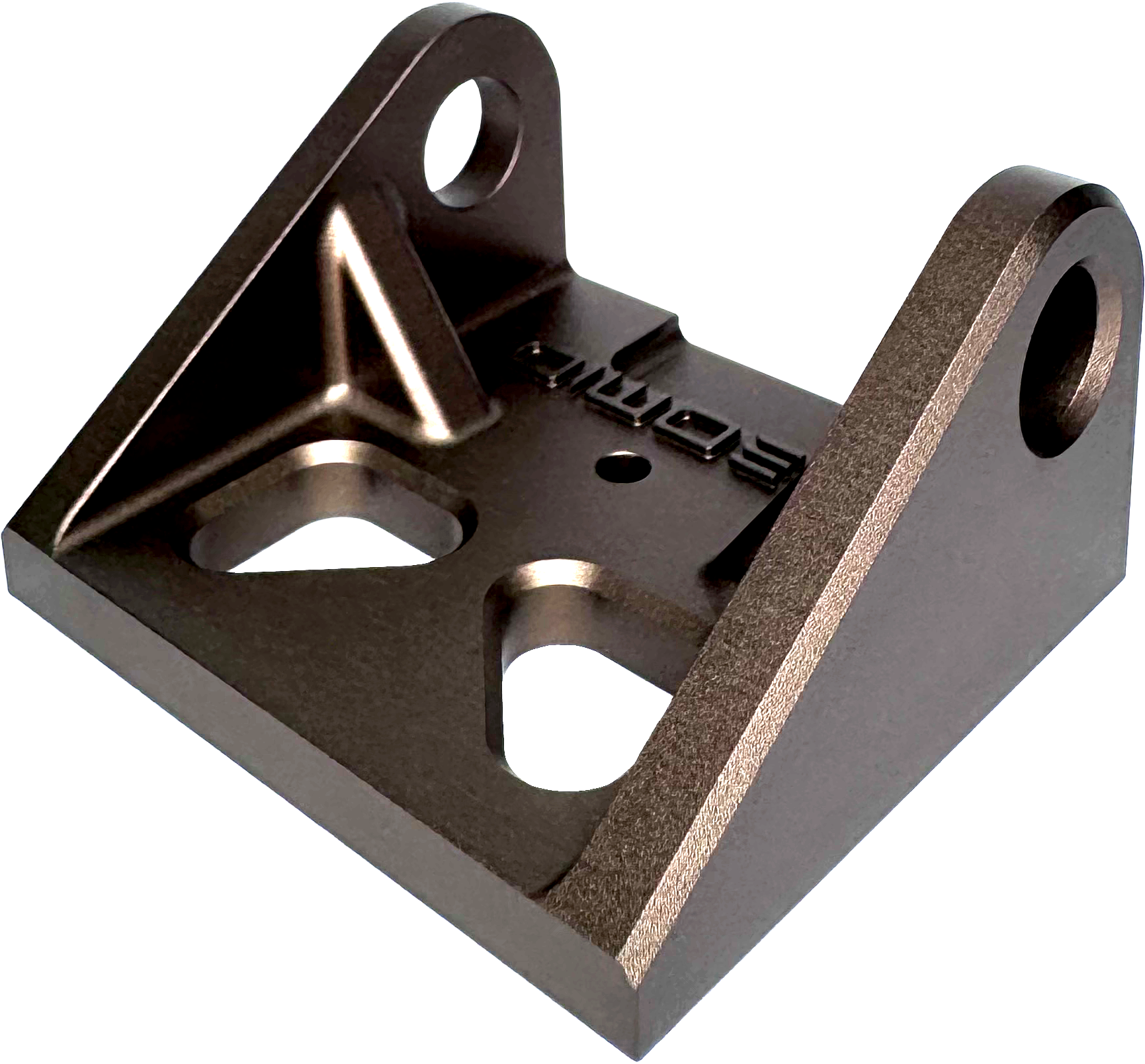
Removes all machining marks & medium texture with bronze dye
Typically used as a pre-treatment process, chromate conversion coating is a great option to prime surfaces before anodising. The below parts have had chromate conversion coating and then been type 2 sulphuric anodised, with additional colour dyes.
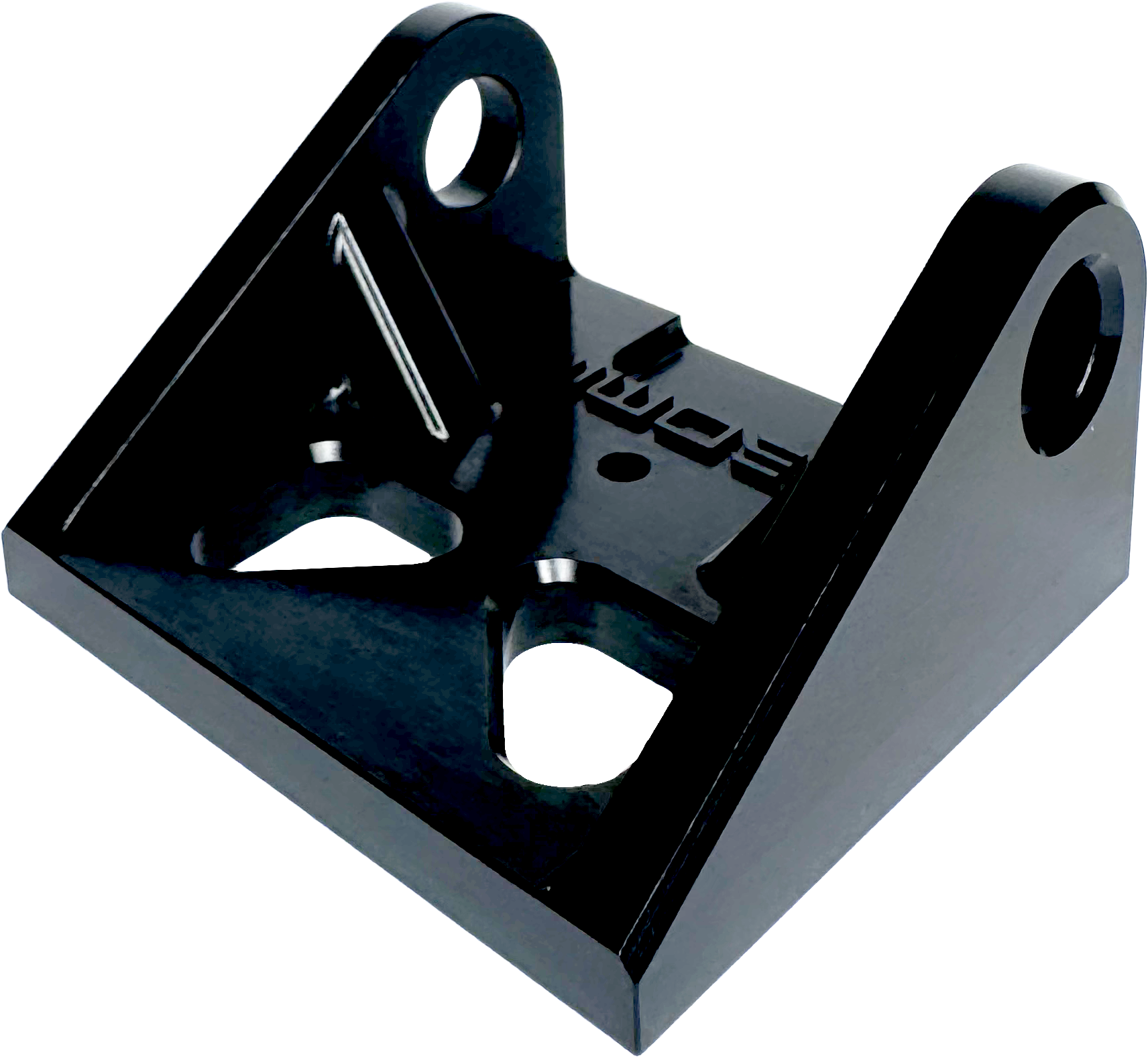

Slightly grainy appearance from the conversion coating with added dye
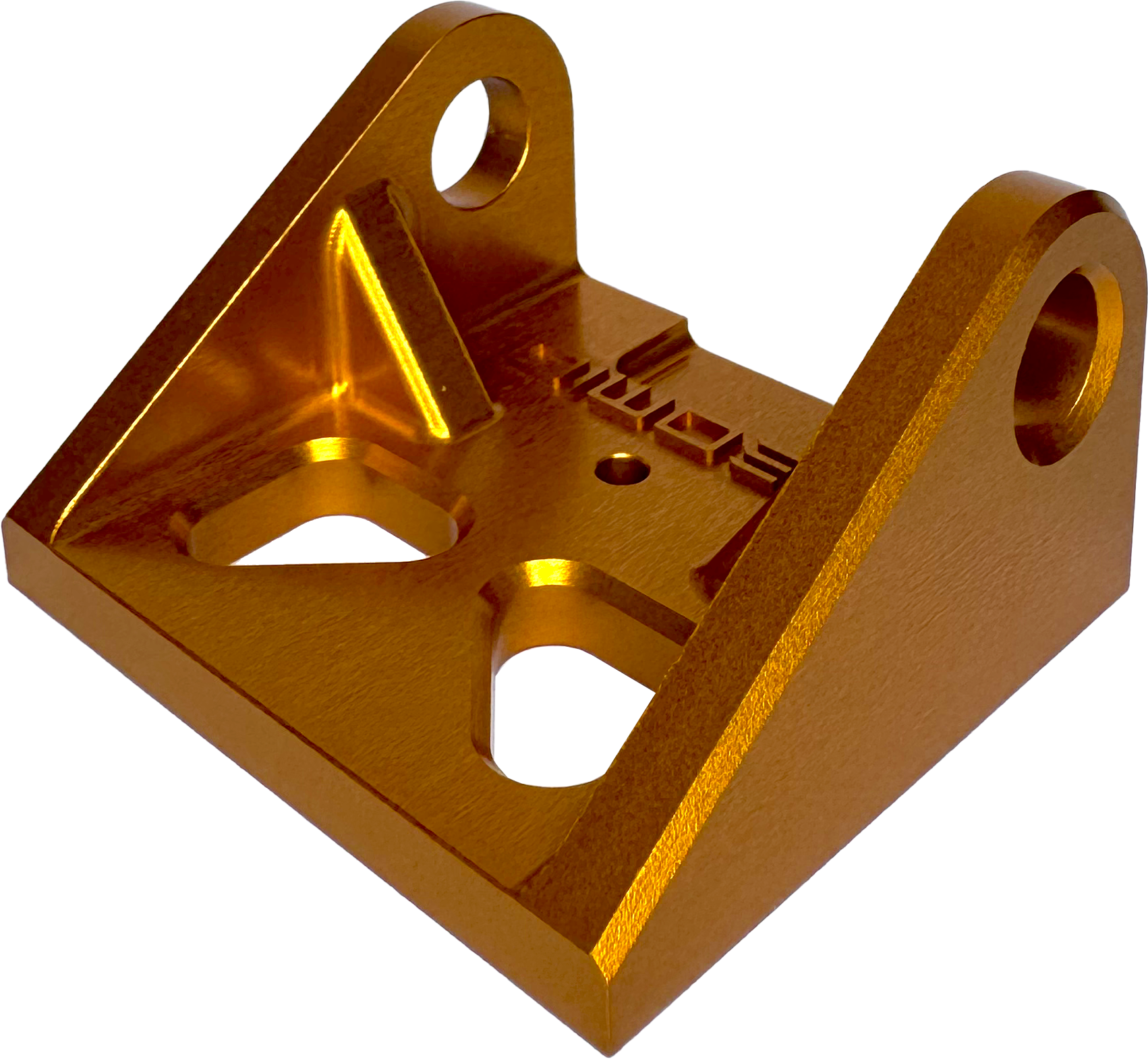
Slightly grainy appearance from the conversion coating with added dye
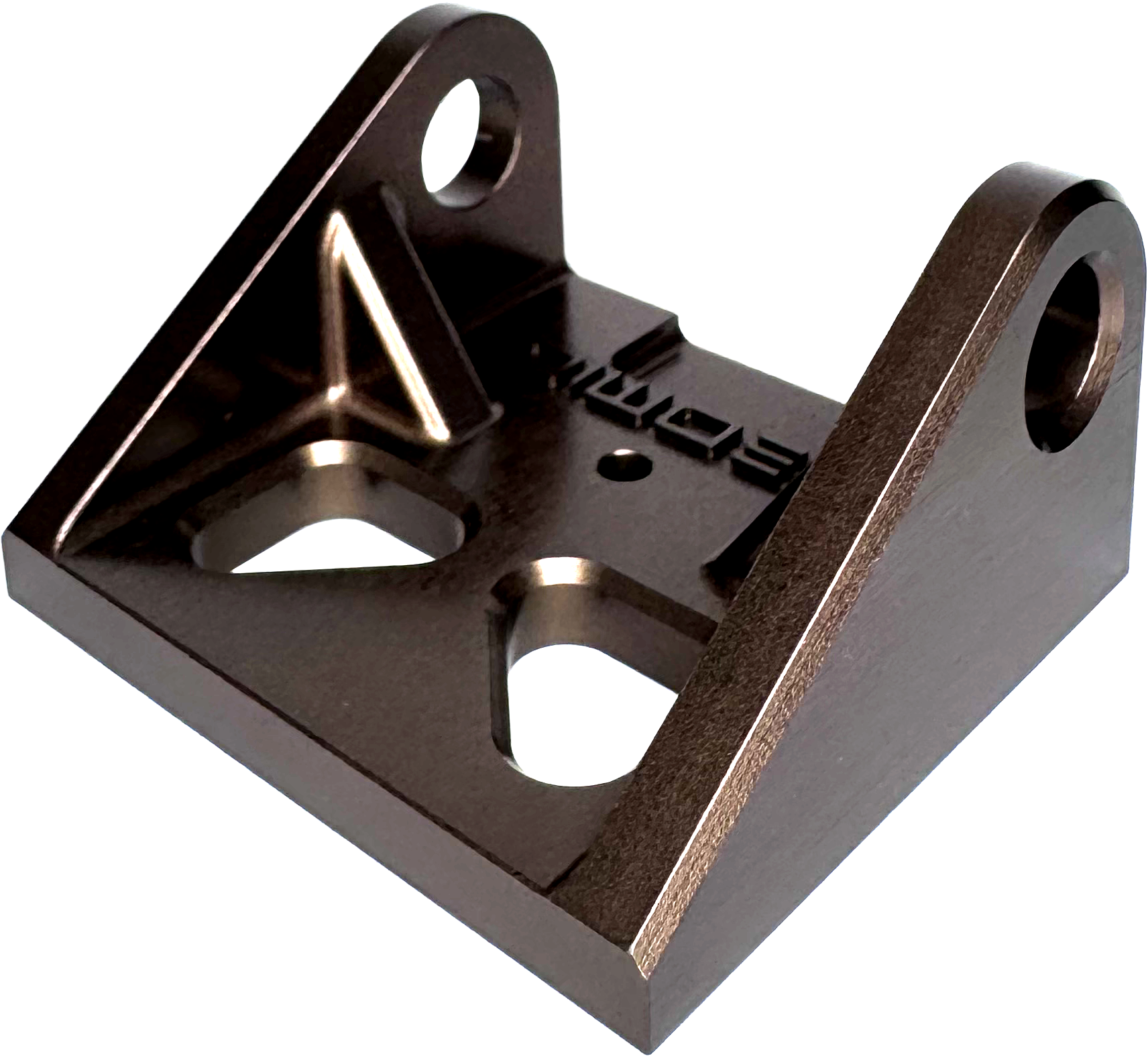

Slightly grainy appearance from the conversion coating with added dye
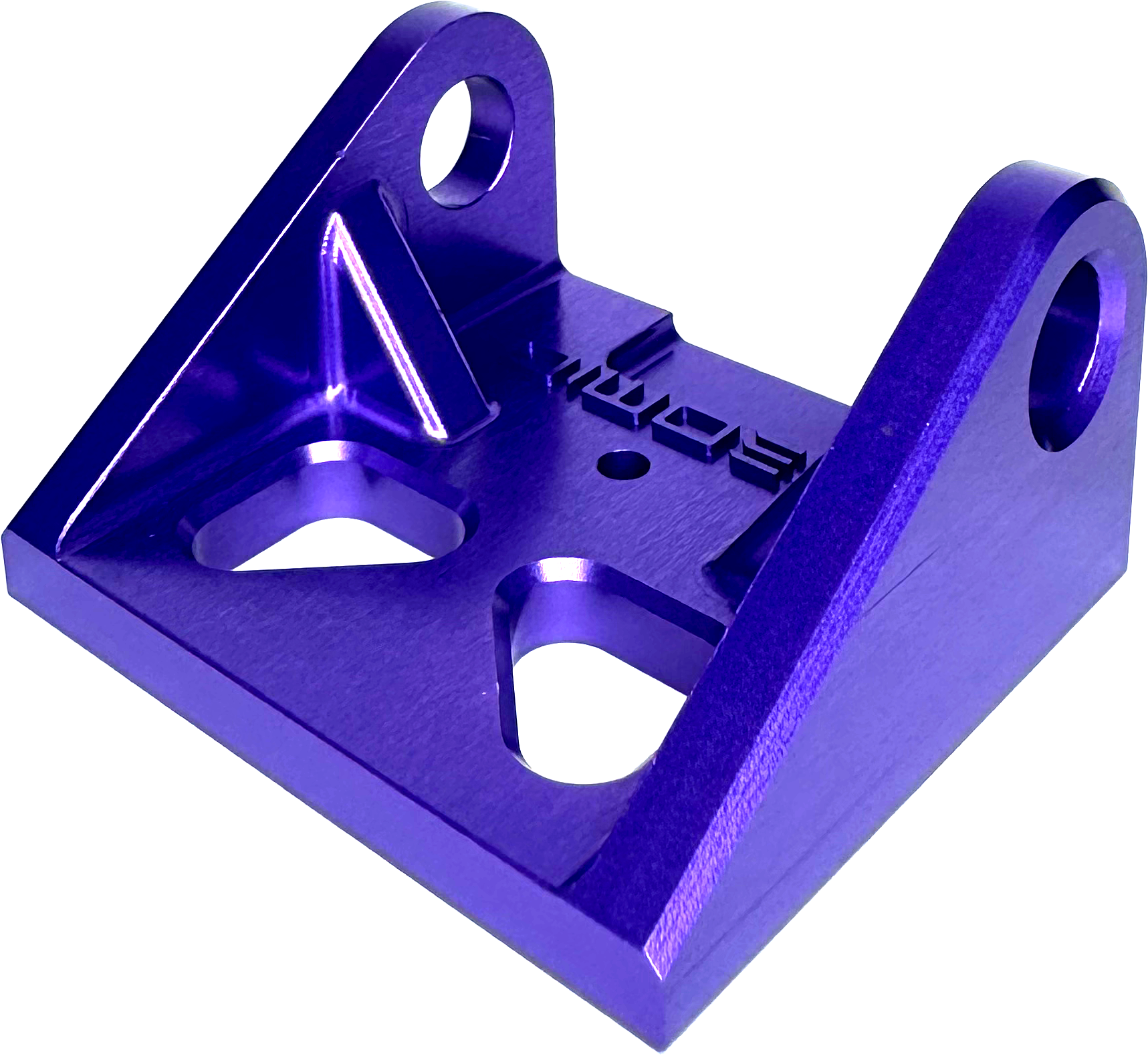

Visible tooling marks and light surface scratches.
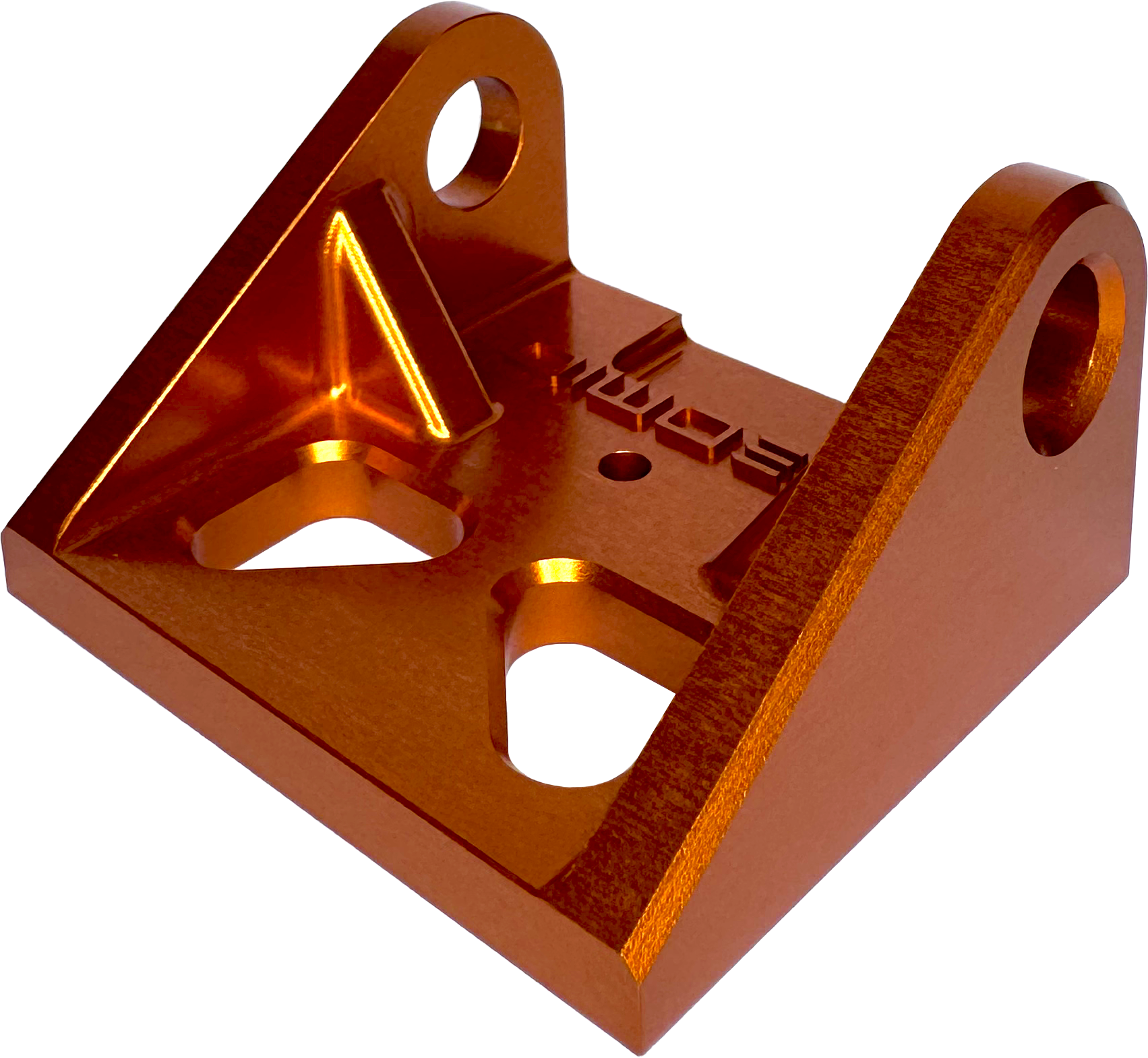
Slightly grainy appearance from the conversion coating with added dye

Black, Grey or colour matched Hard Anodising with the ability to specify exact coating thickness up to 100µm including PTFE coated Hard anodising.
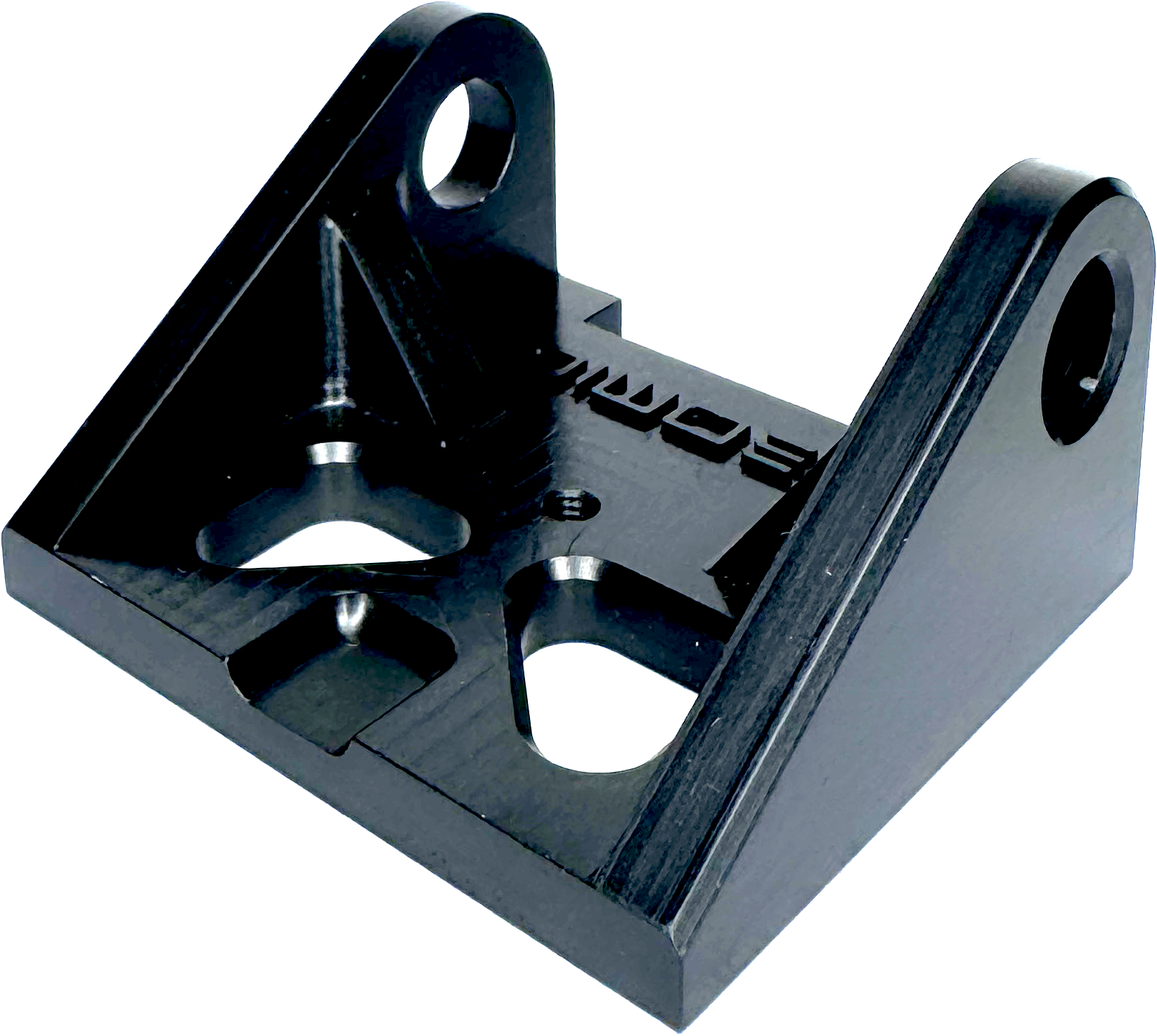

Visible tooling marks or parts can be seen or you can bead blast to create a matte appearance. Slightly grainy appearance from the hard anodising
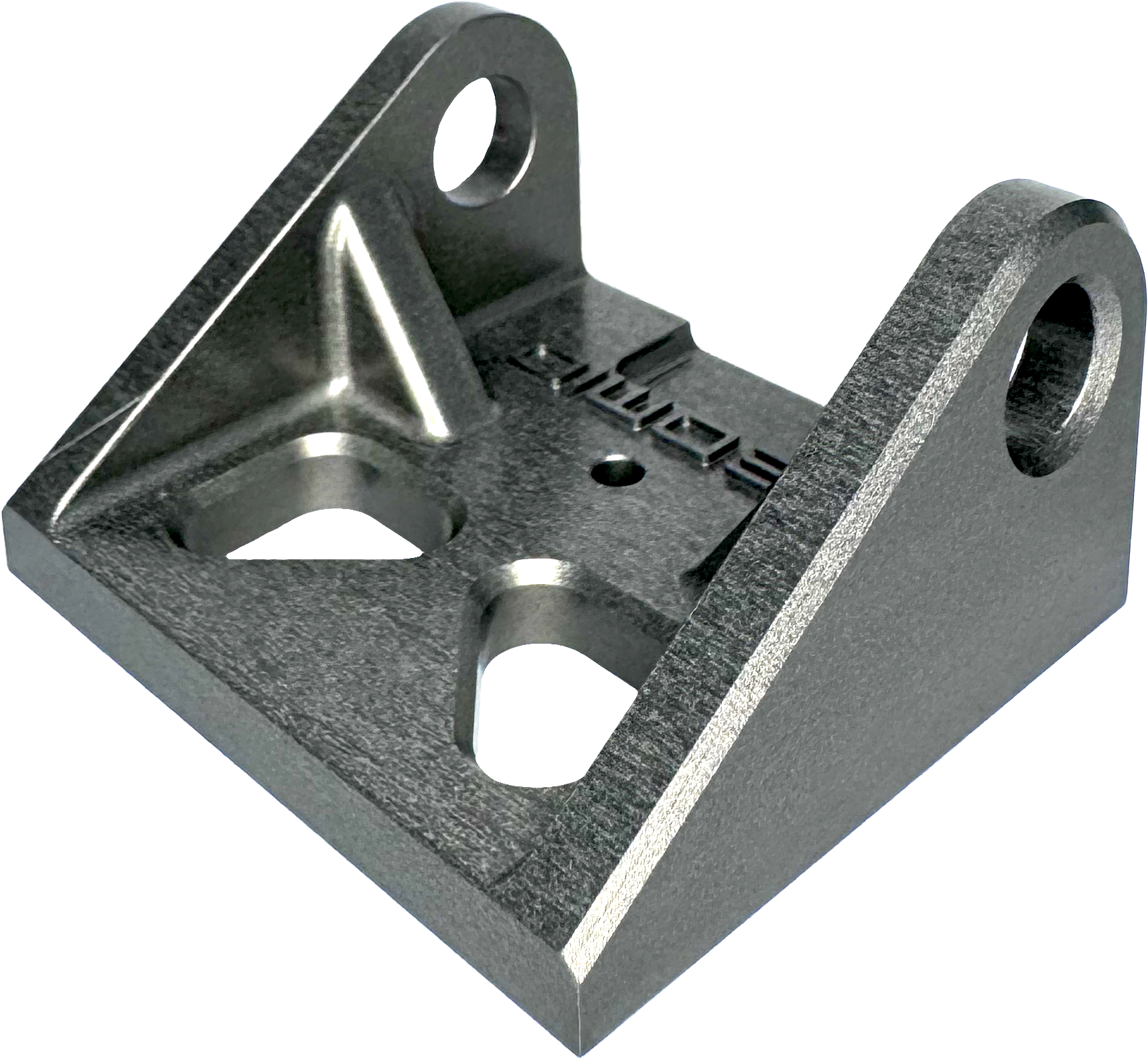

Visible tooling marks or parts can be seen or you can bead blast to create a matte appearance. Slightly grainy appearance from the hard anodising

We also offer Surtec 650, 650V, Electropolishing, Brightening, Iridite NCP, Passivating and Chemical Blackening (Black Oxide coating).
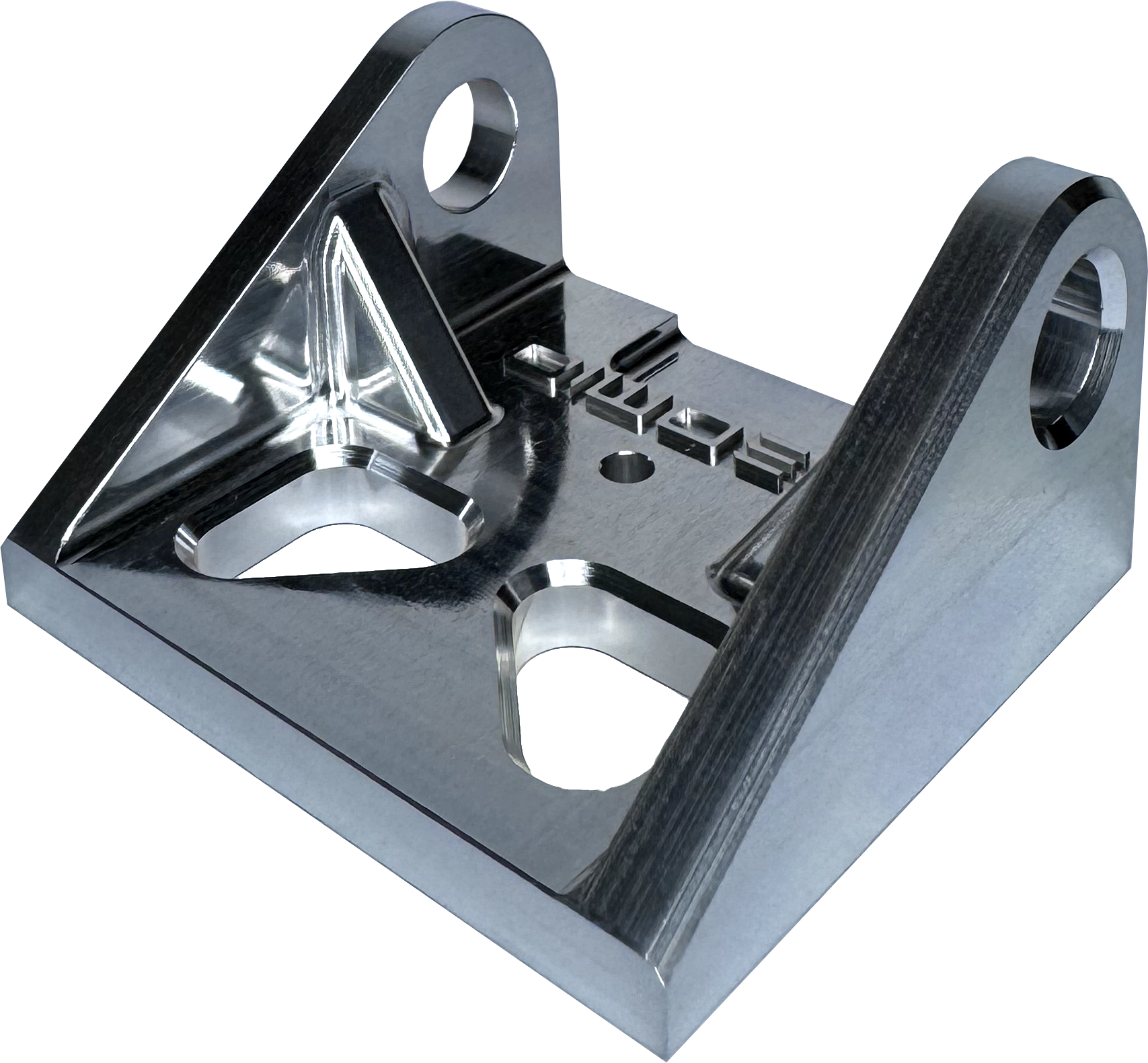
Creates shine and smooths the outside surface of a part by levelling any peaks or burrs. Also increases corrosion resistance
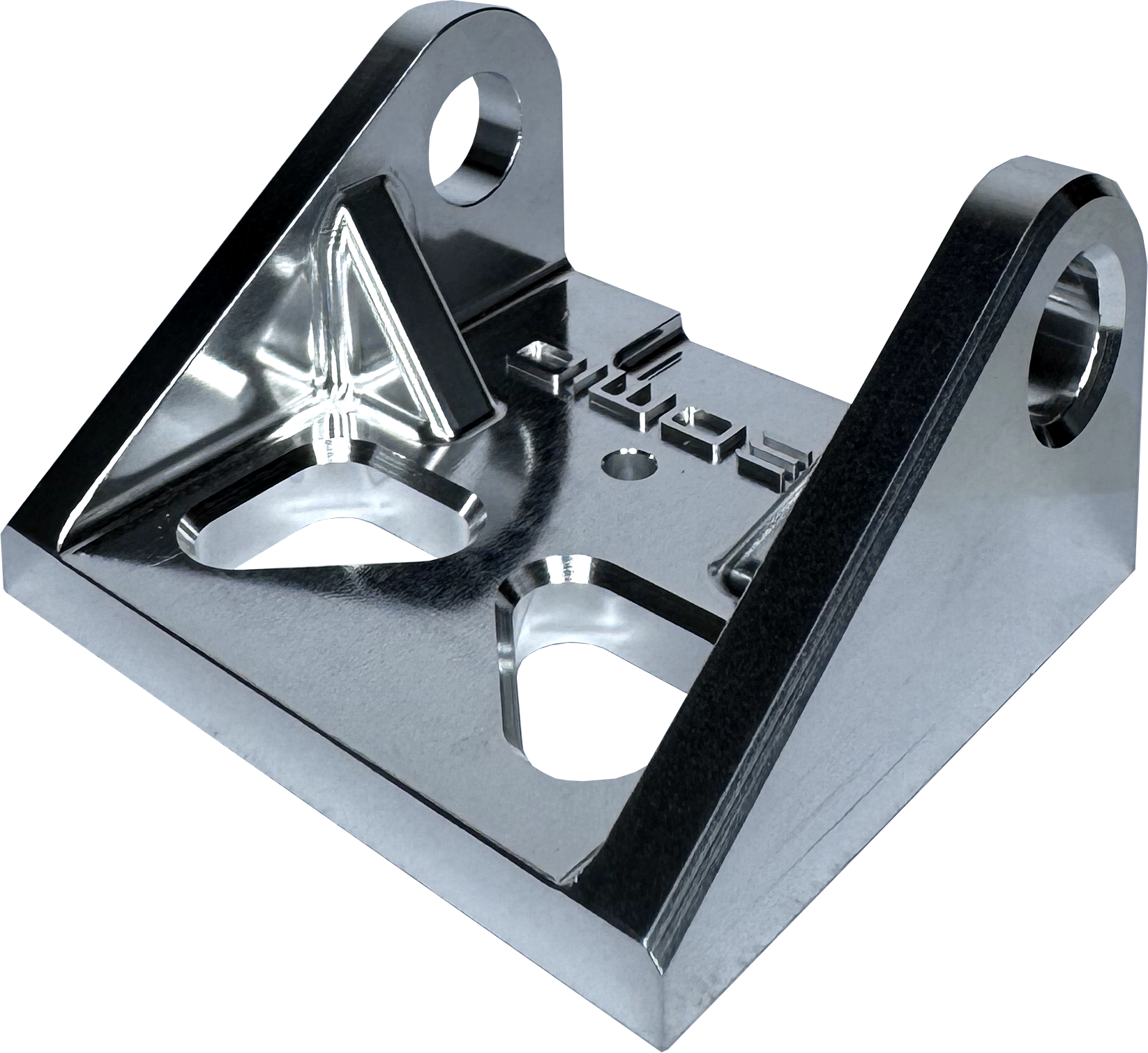

Excellent corrosion resistance, adhesion promotion and non-toxic
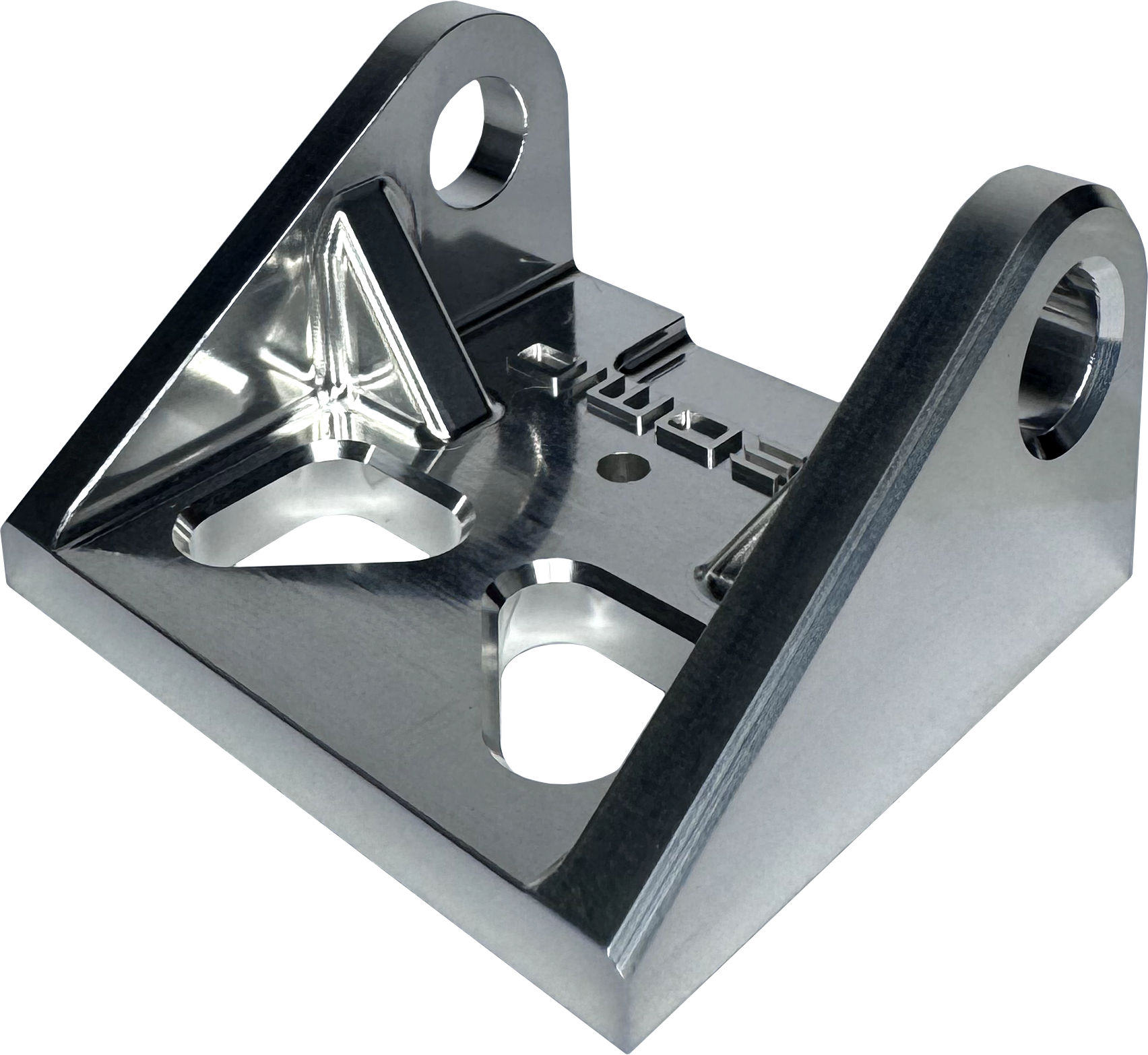
Increases the corrosion resistance by removing surface contamination and adding a micro coating to the surface of the material

A durable coating that has a high level of wear resistance, corrosion resistance and can withstand harsh environmental conditions

A reflective and shiny surface that is often used to prepare parts before anodising
Mechanical finishes are typically for improving aesthetics or preparing a base material for an additional treatment.

A wide range of bead blasting finishes, some are shown in the bead blasting and anodising section above

A great way to de-burr and smooth the surface of parts leaving feint grainy lines
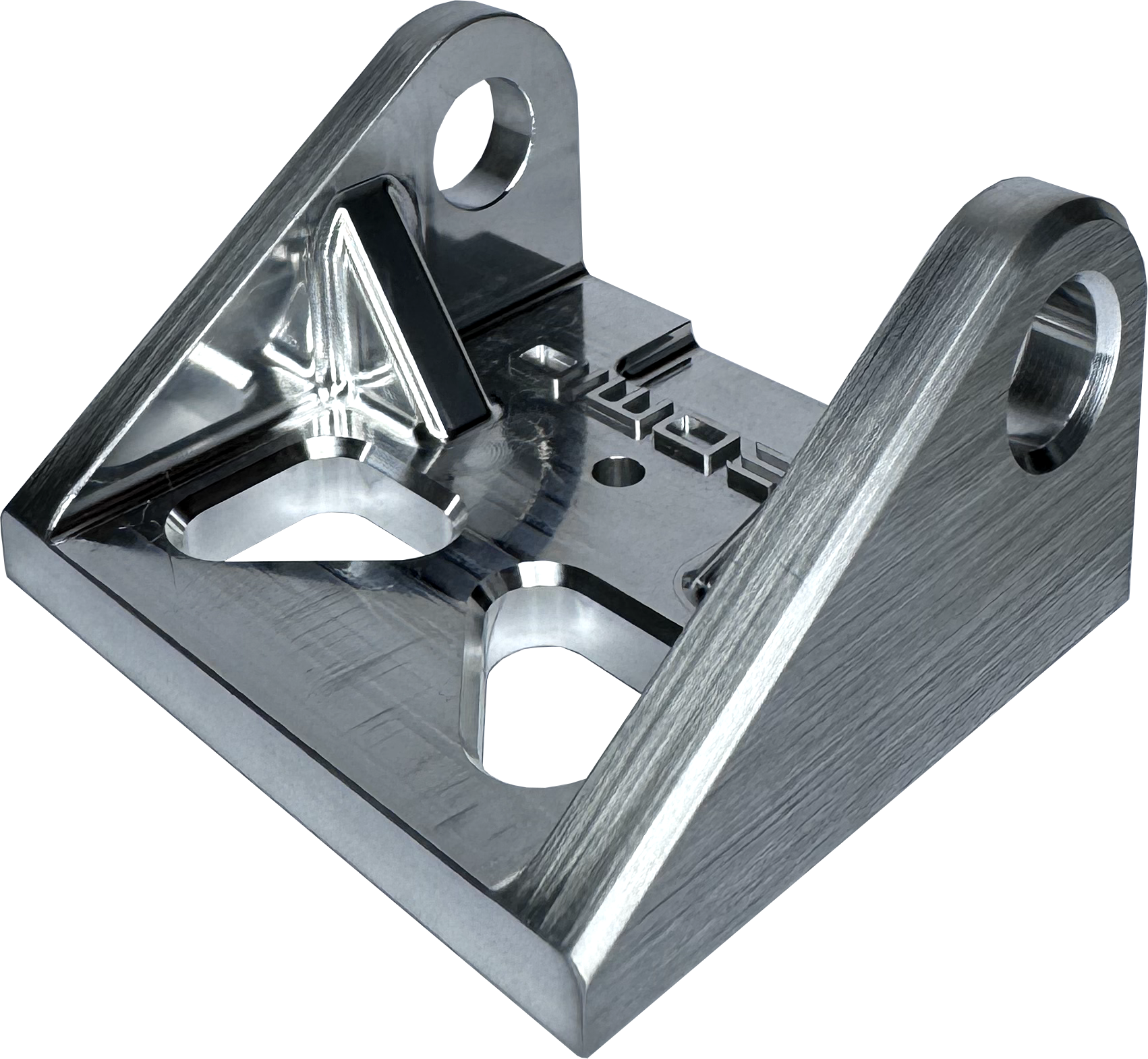
Parts can be linished to have a ‘brushed’ directional appearance
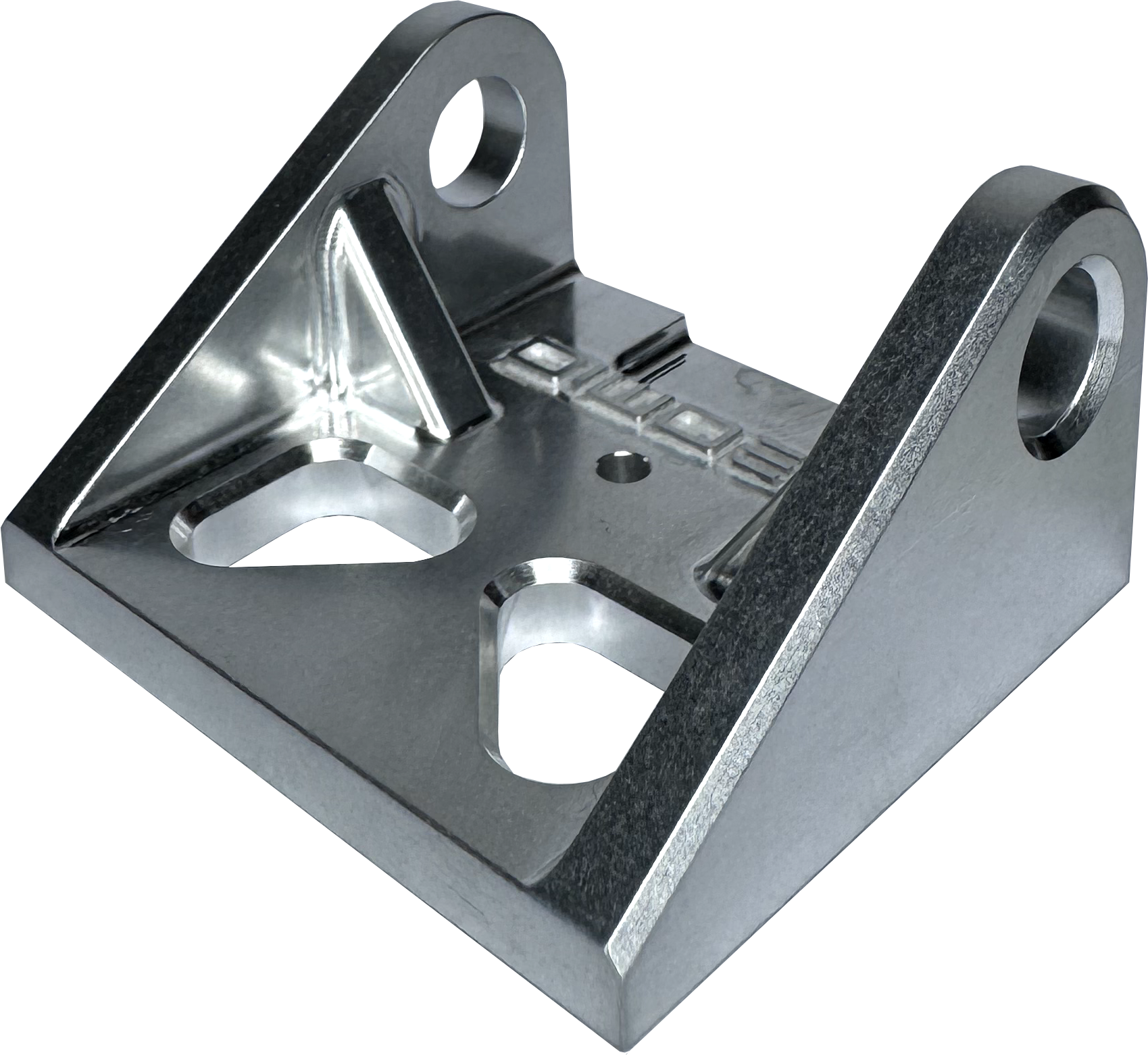

A great way to de-burr and lightly polish the surface of parts
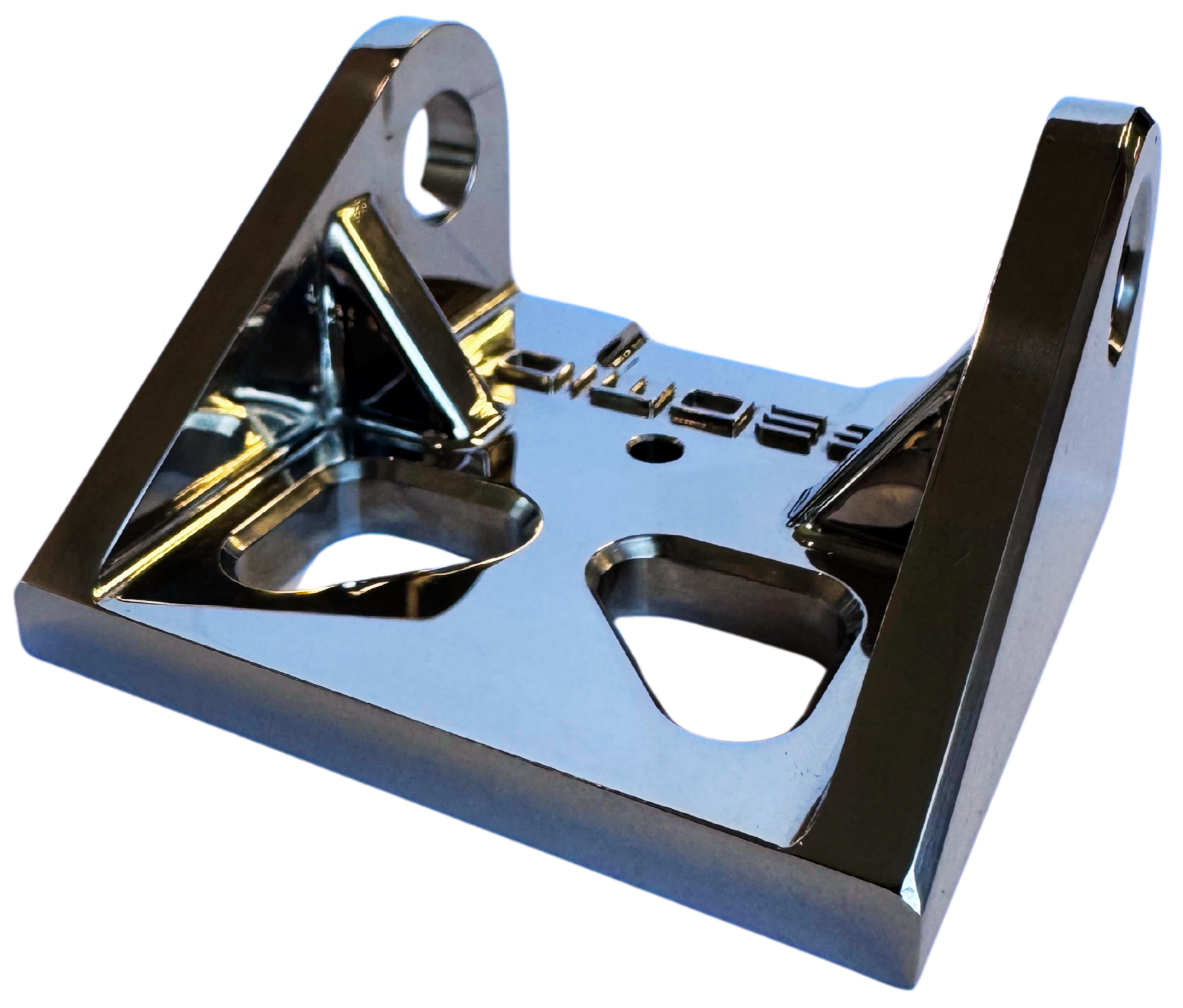

Typically used in the Marine industry on Stainless Steel base material. There should be no scratches or scuffs on the main seen surfaces after polishing.

Etching is a pre-treatment in an acid bath that agitates the surface of the part increasing its porosity and removes most machining marks, and then sulphuric anodised. It is used to create a slightly different appearance to the standard cleaning and anodising process.
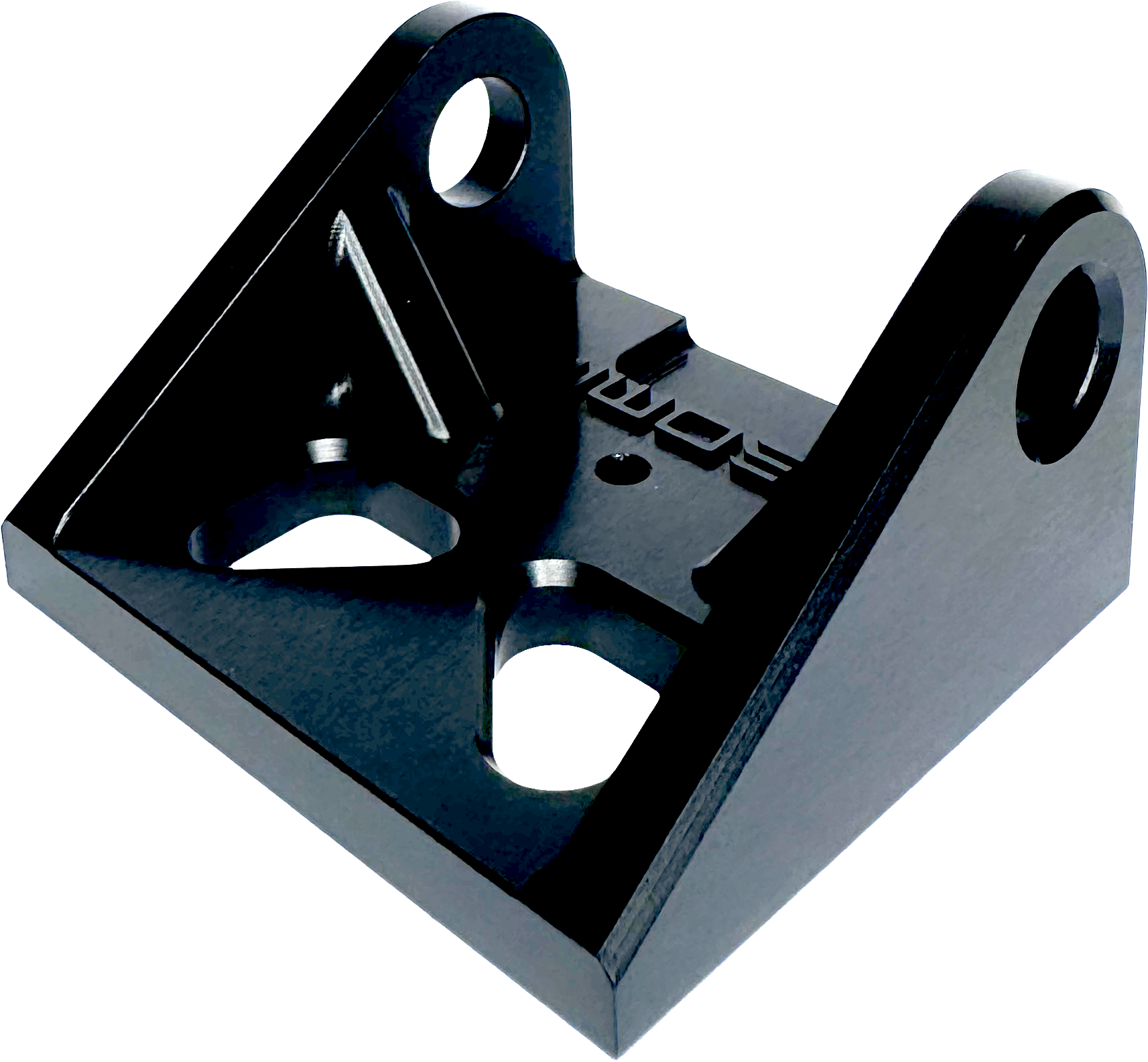

Etched finish has removed most machining marks and has had black dye added to the anodising layer
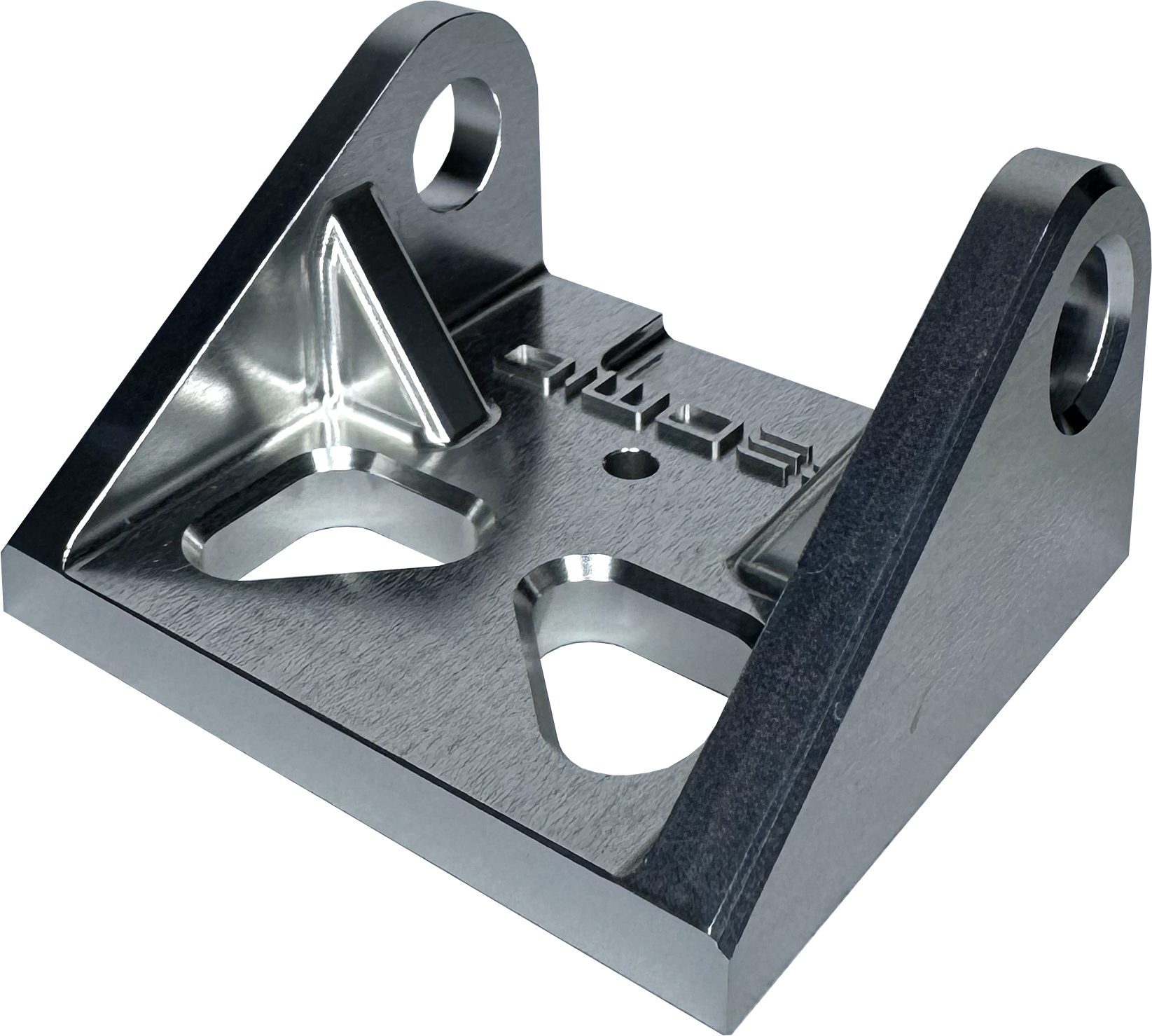
Clear anodised parts are not chemically polished for long, resulting in a dull effect
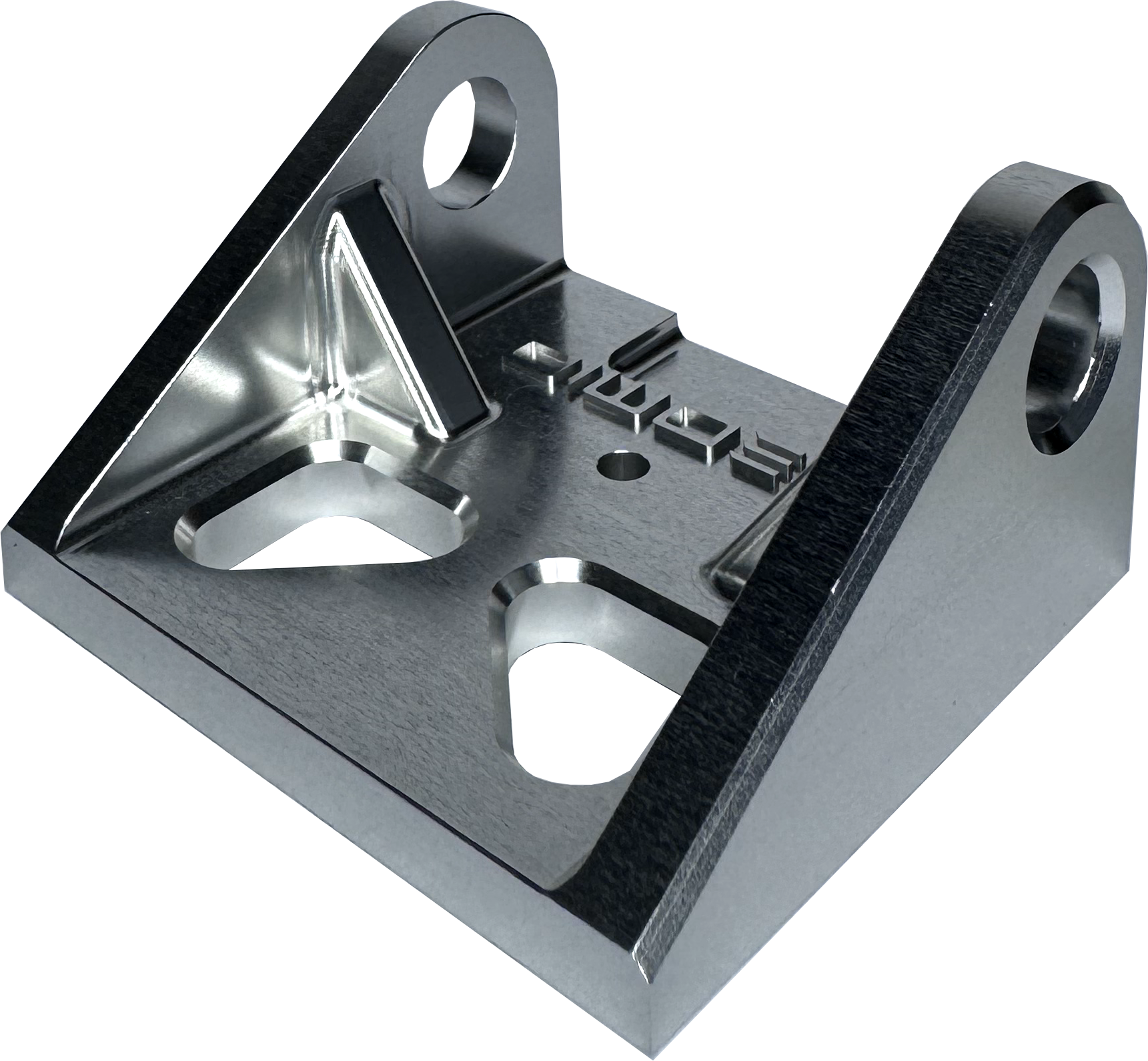
Silver anodised parts are chemically polished for a longer time that results in the base material being brighter prior to anodising

Powder coating provides a continuous and even coating that protects the base material from corrosion as well as improves the aesthetic appearance. All exact match Pantone and RAL colours are available with Powder Coating.
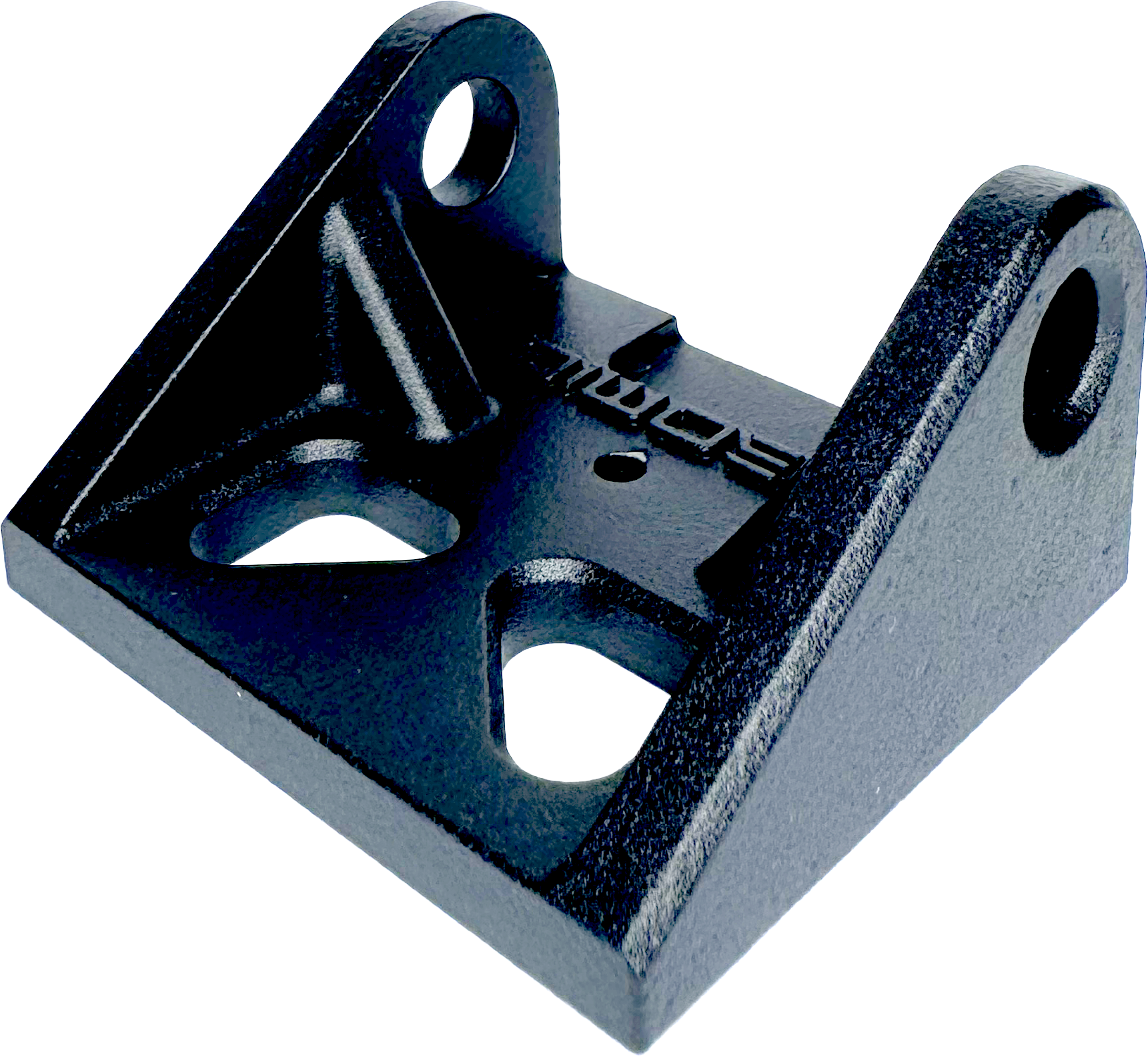
A grainy matte appearance that does not reflect much light.
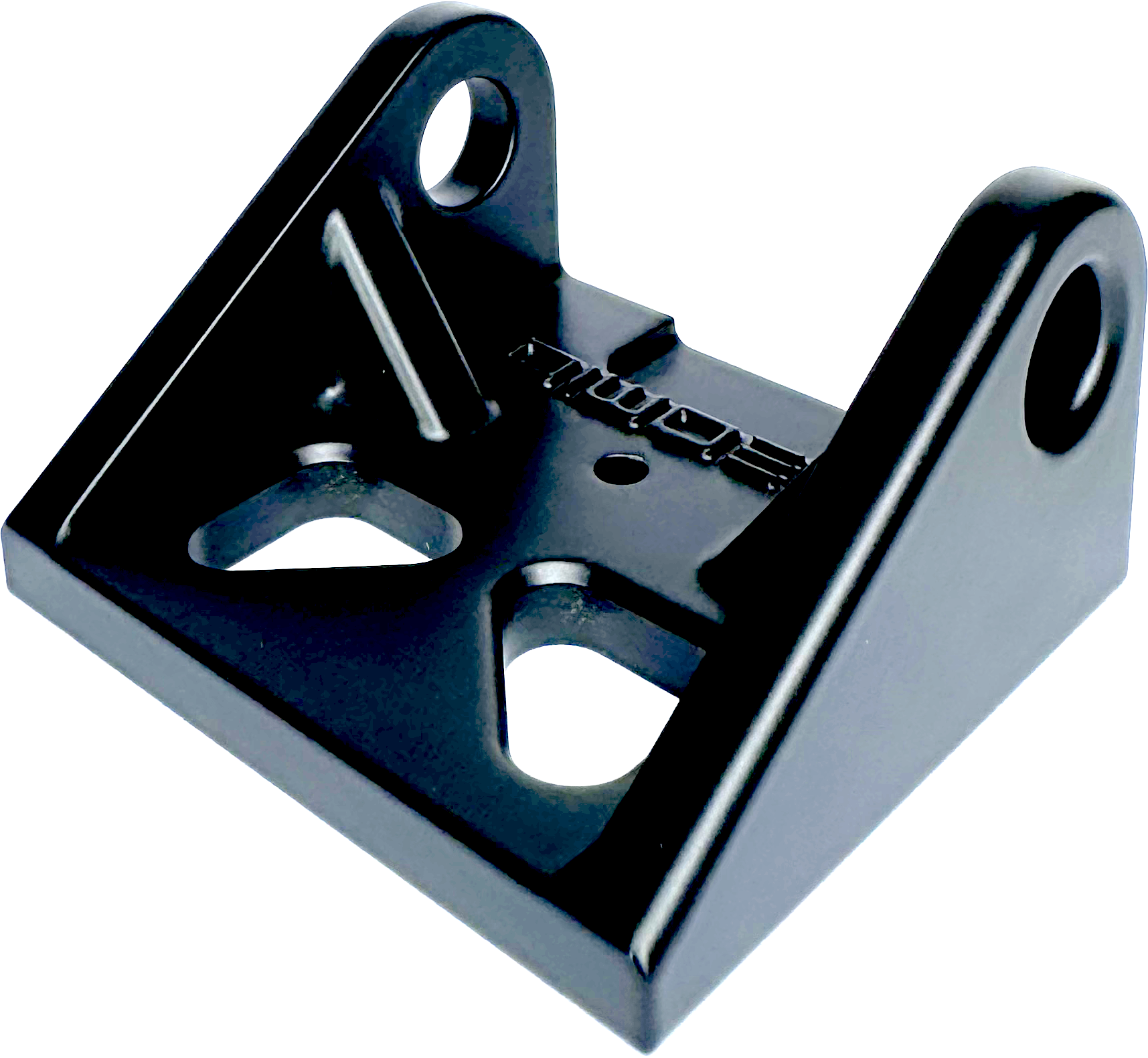
A smooth surface with slightly reflective appearance.
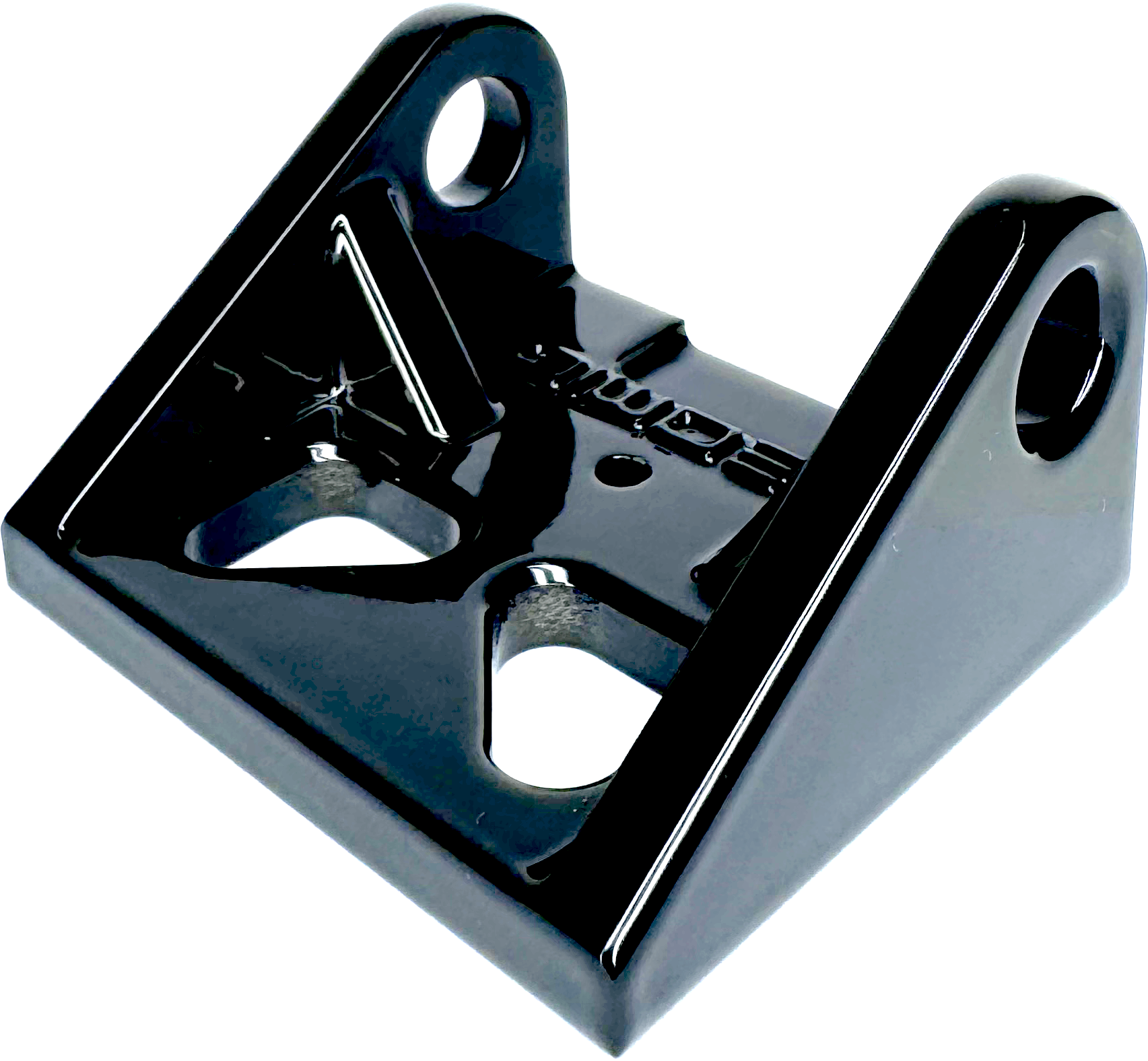

A smooth surface with highly reflective appearance.
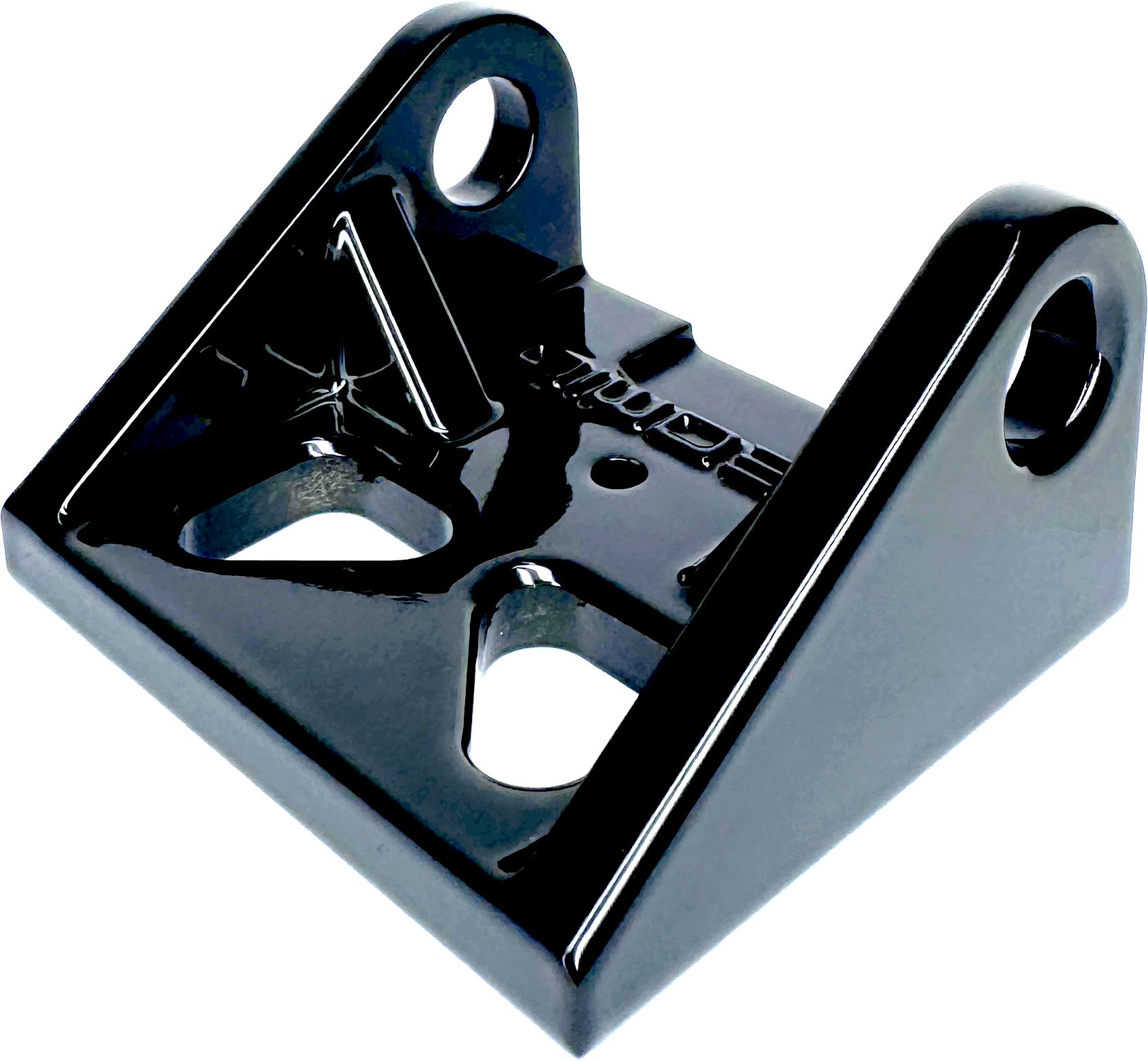
A smooth surface with very highly reflective appearance.
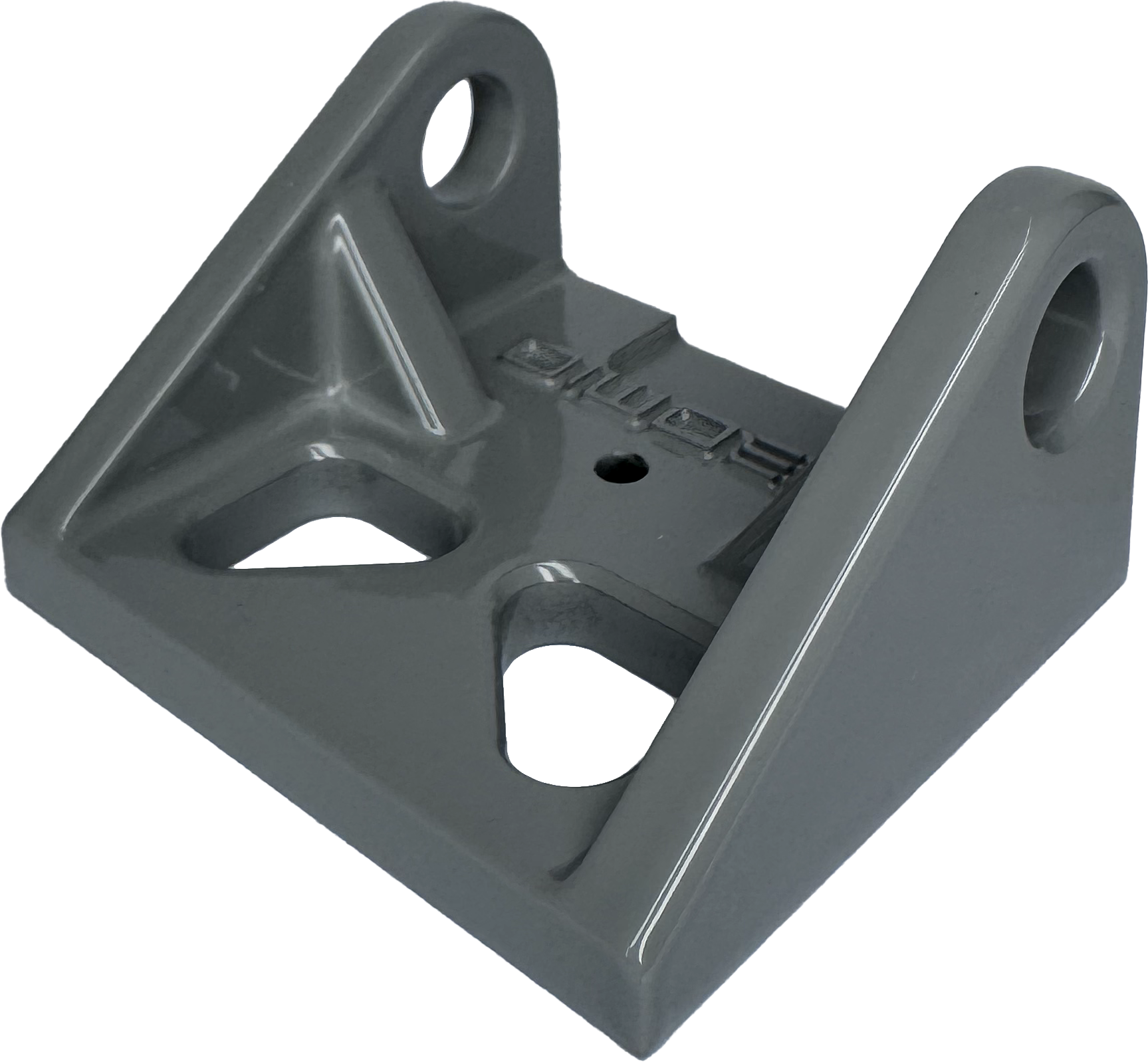

A smooth surface with highly reflective appearance.

A smooth surface with highly reflective appearance.
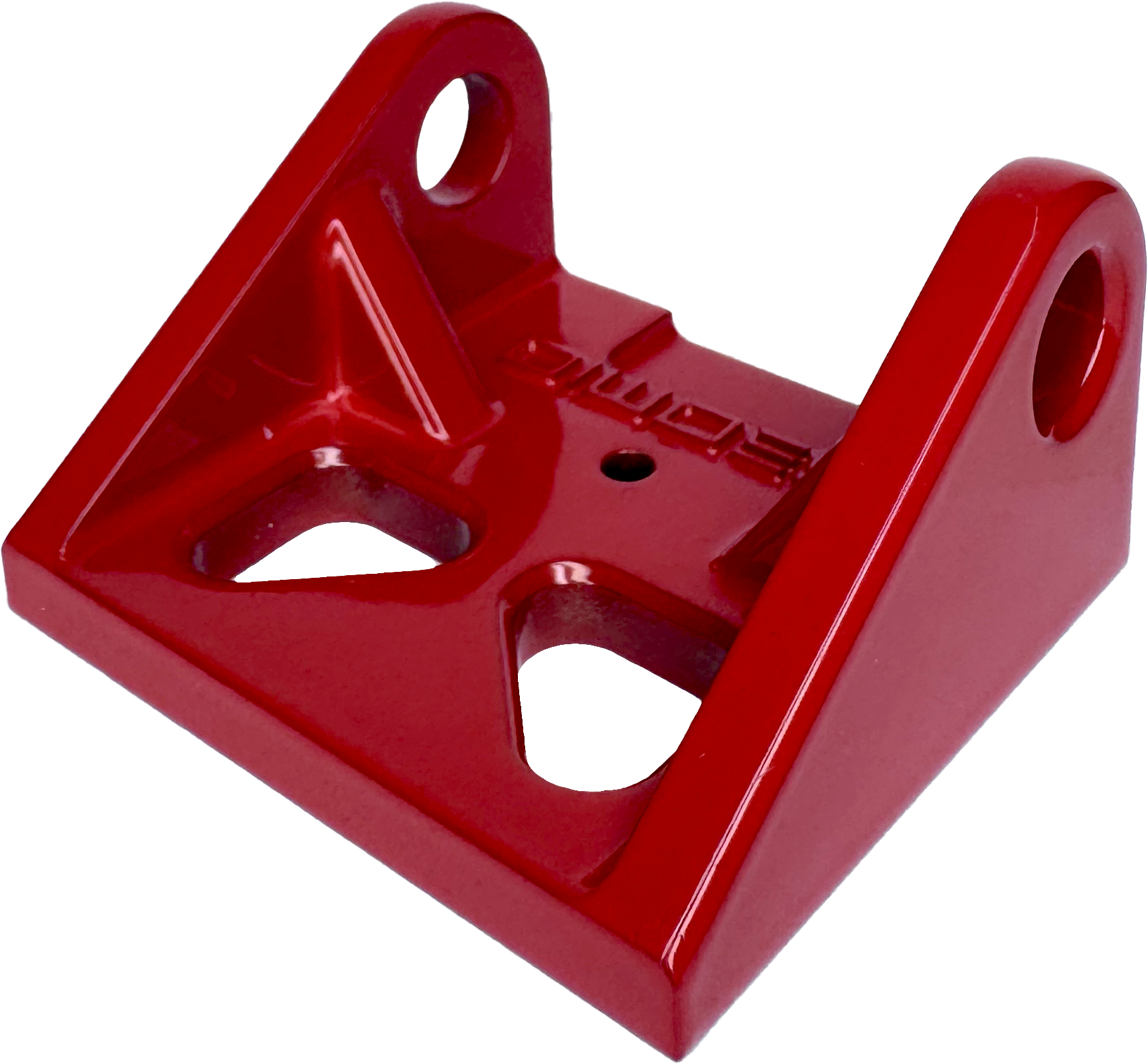

A smooth surface with highly reflective appearance.

Metal plating provides a uniform thickness coating, which offers protection from corrosion, oxidation and wear. Parts will appear brighter than in photos and are reflective.
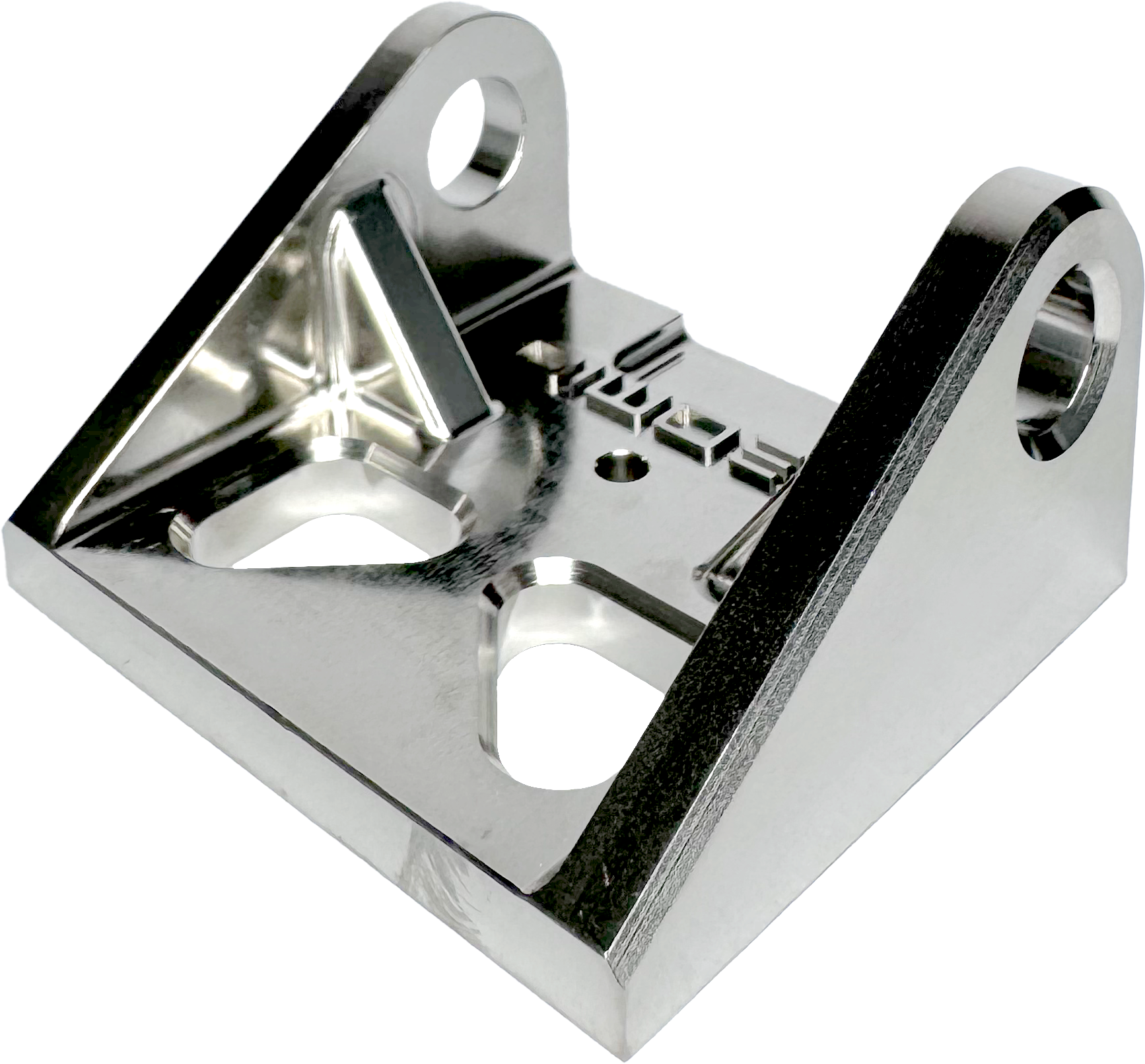

Excellent for corrosion resistance, very cost effective. Has slight reflective surface.
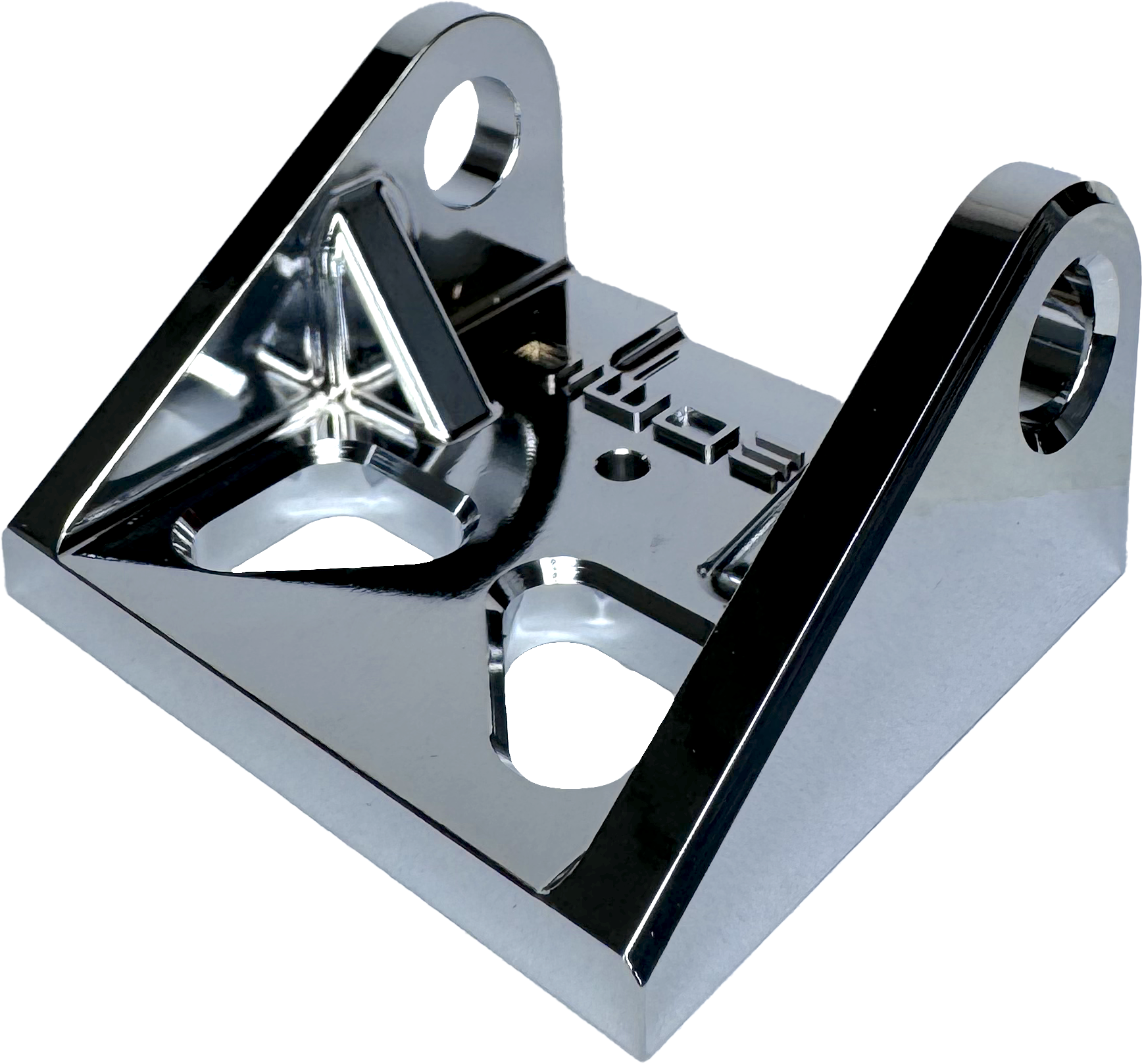

Highly reflective and evenly applied surface finish, similar to mirror polish.

All uploads are secure and confidential.
See our case studies in action. Discover how we turn ideas into products with our prototyping and manufacturing capabilities.
See our case studies in action. Discover how we turn ideas into products with our prototyping and manufacturing capabilities.
Oz Andrews
Director
Tyba Home
We use the Geomiq platform as it is the easiest and fastest way to get any of our parts made. They are the obvious choice, highly recommended!
Jamie Fairclough
Design Lead
Industrial Robotics | Arrival
Geomiq streamlines your parts supply chain down to a single supplier. A true enabler for anyone involved with fast paced R&D through to production.
James Batstone
Future Product Research Lead
Brompton Bikes
Geomiq have been fantastic in getting one-off prototype parts to us in our research team super fast so we can go out and test these ideas in the real world using the Brompton Future Lab initiative.
Alex Leck
Design Engineer
JCL Lighting
The quality and service since using Geomiq has rapidly accelerated our development process for roadmap, strategic and bespoke projects.
All uploads are secure and confidential.